Robotic welding trending towards automated sensing
By Staff Report August 31, 2024 11:45 am IST
According to Dr. Krishnan Sivaraman, Industrial Welding Expert and Associate Dean – R&D and Industrial Liaisoning, technology and digitalisation are introducing new dimensions to the craft of welding. From robotic welding to AI integration, these advancements reshape workflows and ensure higher quality standards.
Which latest trends and innovations are impacting the welding automation systems?
Welding is an essential part of the manufacturing and construction industry. Advancements in technology are improving quality and productivity and making it necessary.
Over the years, the ongoing quest for efficiency has led to the development of increasingly effective welding techniques. Today, robotic welding is evolving as a prime example, utilising computer control to execute welding with unmatched speed and precision. This approach amplifies efficiency and minimises risks to human welders. The shortage of skilled welders and a competent workforce worldwide continues to be a significant challenge for the manufacturing industry. In response, companies are increasingly turning to industrial automation, such as robotisation and automation of welding processes. The lack of skilled welders alone is a compelling reason businesses invest in automation solutions.
In a nutshell, the heavy manufacturing and welding automation industry is witnessing a transformative phase. Companies are navigating challenges through innovative solutions, adapting to the need for skilled workers and flexible production processes, and redefining the role of welders in the age of automation and technology.
What market growth do you perceive for welding robots and other innovative welding technology?
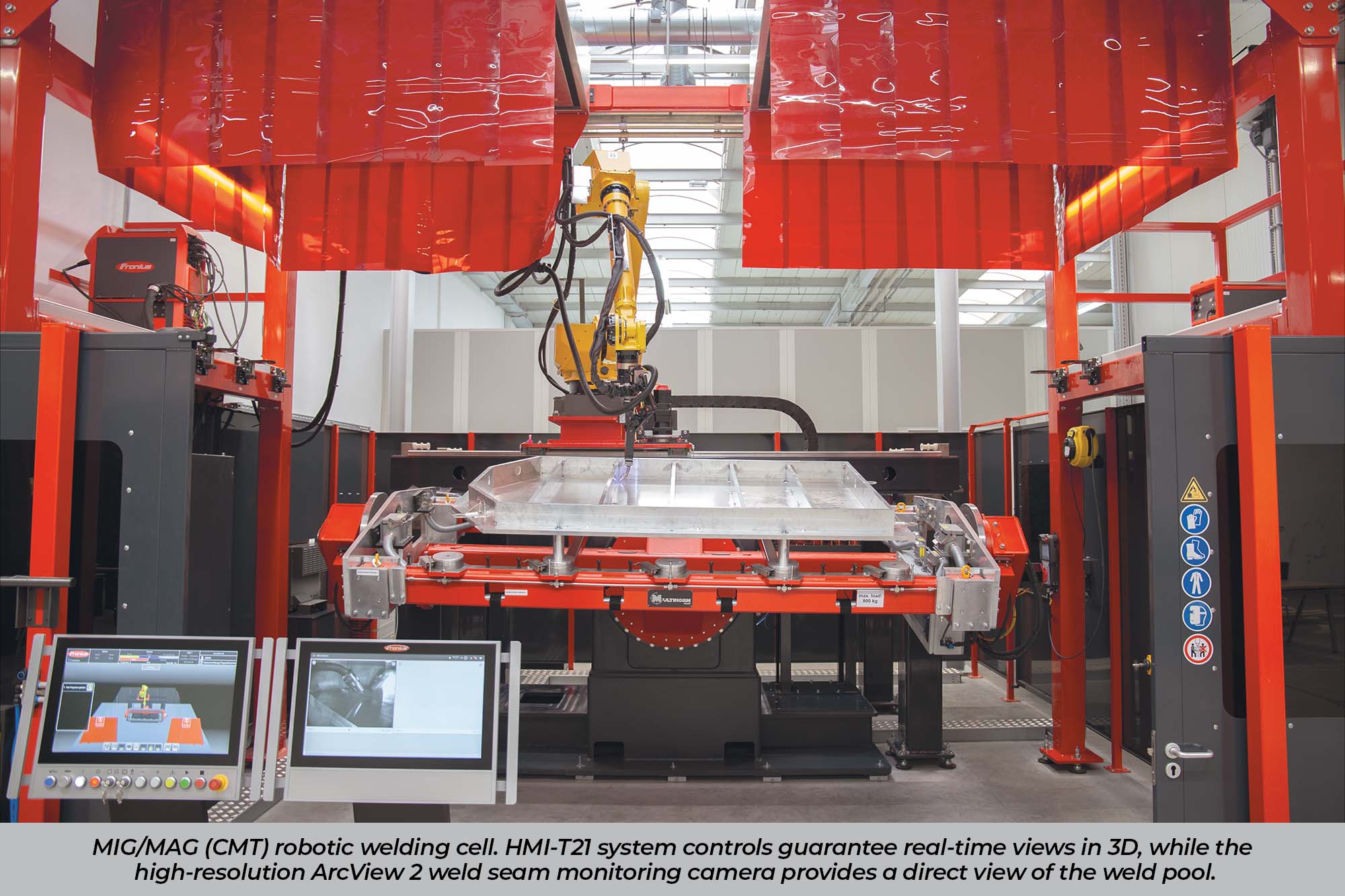
Innovation in welding equipment is driven by the pursuit of efficiency, precision, and safety. Welding torches, for instance, have revolutionised, integrating advanced power sources, digital controls, and pulse welding technology. These enhancements streamline the welding process, offering welders improved control and optimal performance. Trends in Robotic welding are towards eliminating fixtures, automated sensing for improved weld quality, real-time data acquisition and analysis, and improvements in Ease-of-Use with collaborative robots(Cobots).
The global robotic welding market is growing, with the rapid development of emerging manufacturing economies as a key driver, according to a report from a market intelligence firm. As reported by market analysts, the global robotic welding market is expected to grow from $5.80 billion in 2021 to $9.76 billion in 2028 at a CAGR of 7.7 percent in the forecast period 2021-2028. The report forecasts that the robotic welding equipment and peripherals market will grow to $11.57 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of approx. 11.5 percent during the forecasted period of 2023-2028.
How do you evaluate the growth of automated welding manufacturing?
India now presents itself as a favourable destination for foreign companies. This is due to streamlined regulatory processes, an abundance of talent, joint research and development opportunities, and the capacity to manufacture and assemble high-quality products meeting international standards. Industry experts and market analysts have dubbed the current phase the ‘golden era’ of India’s industrial boom.
Industrial experts report that positive changes in the manufacturing sector, including increased merger and acquisition activity, supportive government policies, expanded production capacity, and substantial investments from private equity and venture capital, are building a foundation for the nation’s long-term economic success. These developments are key in enhancing competitiveness, fostering innovation, and driving sustainable growth across the industry.
In the dynamic world of manufacturing, efficiency and productivity are the keys to staying ahead of the competition. With the rise of Industry 4.0 and digital transformation, automation has emerged as a significant catalyst in reshaping the manufacturing landscape. Industry 4.0 refers to integrating advanced technologies like robotics, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) into manufacturing processes to improve productivity and quality.
Automation in manufacturing refers to technology and machinery that perform tasks previously done by humans. The automation goal in manufacturing is to increase efficiency, productivity, and quality while reducing labour costs and improving safety. automation in manufacturing can be classified into three categories: fixed, programmable and flexible. While fixed automation refers to specialised equipment to perform a single, repetitive task, programmable automation uses equipment that can be reprogrammed to perform different tasks. Flexible automation utilises robots and other advanced technology to adapt to changing production needs.
Please discuss strategies to create a culture of continuous learning and upskilling workers.As welding technology continues to evolve, several sectors are experiencing a high demand for skilled welders equipped with expertise in cutting-edge techniques. These emerging sectors are at the forefront of adopting welding innovations to enhance their operations and achieve greater efficiency. The American Welding Society projects that the shortage of skilled welding operators will reach 400,000 by 2024. Not to mention, the ageing workforce produces a great need for more skilled welders, especially since the average age of a welder is 55.
In workshops, there is a noticeable shift from humans solely as welders to becoming operators. Technology and digitalisation are introducing new dimensions to the craft of welding. While welding skills remain crucial, they are now utilised to assist automation in performing specific tasks. When companies invest in welding automation, the role of the welder evolves into that of an operator. The welding operator’s skills remain vital, particularly in the offline programming of robotic cells. Furthermore, an essential skill for welders in the future is a positive attitude, curiosity, and a willingness to learn new things. Creating a culture of continuous learning and upskilling the knowledge of the involved workforce is the need of the hour for any Industry to sustain itself in this highly competitive global market.
How are Smart factories evolving with AR and autonomous robotics welding implementation and cobots?
Training more welders to join the workforce is time-consuming, risky, and expensive. With the rise of virtual and augmented reality technologies, this training can occur in a contained space under expert supervision. At the same time, an organisation can use VR and AR technologies to simulate real-world environments, allowing welders to practice before taking on more complex projects. Ultimately, these types of training can reduce human error and increase productivity. Besides these innovations, organisations can also expect advancements in laser sensing technologies. It will allow them to produce higher-quality welds while giving workers increased access to real-time data and analytics. It can help them detect errors and correct welds with ease.
Automation is not likely to replace a manual workforce. With the rise of cobots, a skilled welder can work with a robot to automate repetitive and mundane tasks. While the robot eliminates human error and can work in more hazardous environments, a highly skilled welder can focus on more complicated tasks. A cobot is cheaper than a robot but still offers high efficiency.
Please discuss the role of advanced materials and techniques in modern welding processes.
In recent years, metal fabrication shops have begun to use new and advanced materials. Alloys and composite materials are more durable, corrosion-resistant, and lightweight than traditional metals, providing a significant advantage in manufacturing and construction. However, these new materials come with new welding challenges and necessitates innovative techniques to achieve optimal results. The welders need education and training on how to work with these new materials.
Changes in work materials over the past ten years have driven improvements in welding, many of which are impossible to apply manually, such as laser welding. The manufacturers of everything from mining vehicles to automobiles to space vehicles use different materials to reduce cost and weight and to accommodate different powertrain solutions. Automotive manufacturers have switched to more high-strength and ultra-high-strength steels with metallurgical properties. That makes them stronger, lighter, and more corrosion-resistant, with high formability and weldability. For arc welding, power sources are now advanced and electronically controlled. The deposition of material into a weld pool is carefully controlled, with customised waveforms which can reduce distortion and improve the cosmetic appearance of welds. In short, welding processes and techniques are evolving in tandem with the evolution of new and advanced materials.
Are AI and welding technologies opening up opportunities in industries working with sensitive metals?
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI and ML) are enabling welding robots to learn and adapt quickly, enhancing their capabilities and efficiency. Welding processes are also evolving with the integration of digitalisation. It is revolutionising workflows and improving efficiency in welding operations. Environmental consciousness is happening everywhere, even in the welding industry. Therefore, sustainability and green practices have become crucial considerations.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has recently been used in the welding industry, helping to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality. AI in welding includes algorithms, sensors, and machine learning to optimise the process. AI helps to identify defects, adjust settings, and predict future needs. AI can help optimise welding parameters and perform automated inspections of welds. AI currently has limitations due to the complexity of the technology and the need for specialised training, but shops investing in implementation are seeing high-quality results.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.