Saving OPEX for a reputed Pharma Giant using bioaugmentation
By Staff Report September 11, 2024 2:19 pm IST
A reputed pharma giant partnered with Team One Biotech to enhance their wastewater treatment efficiency using bioaugmentation, reducing COD/BOD, scaling in MEE, and commodity costs. This resulted in 20% OPEX savings and improved overall treatment performance.
The reputed pharma giant is known for contributing to the pharma sector worldwide. This unit is one of the largest API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients) producers that manufacture products such as Tamsulosin, Metformin, Esomeprazole, etc. The unit has a full-fledged ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant), a traditional ASP system. It also treats its wastewater religiously. The unit had an MEE (Multi Effect Evaporator) installed to treat the high COD (Chemical oxygen demand) stream. Due to the production of multiple products, the ETP received multiple effluent streams with tough-to-degrade pollutants like toluene, benzene, Metformin, Acetic Acid, Methanol etc. Due to such streams, it was difficult for them to control ETP operations leading to heavier expenses specifically on the MEE part as it was receiving a heavier load compared to its capacity.
ETP details:
The industry had primary treatment, biological treatment, and then a tertiary treatment.
| Flow (current) | 450 KLD |
| Flow (design) | 500 KLD |
| Type of process | ASP |
| No. of aeration tanks | 3 (in series) |
| Capacity of aeration tanks | 500 KL, 450 KL, 300 KL respectively |
| Retention Time | 67 hours(combined) |
MEE Details:
| Capacity (current) | 12 KLD |
| Current inflow | 10 KLD |
| Inlet COD | 150000 ppm |
| Inlet TDS | 60000 ppm |
Challenges:
| Parameters (PPM) | Avg. Inlet parameters | Avg. Outlet parameters |
| COD | 18000 | 9900 |
| BOD | 5000 | 3000 |
| TDS | 15000 | 9500 |
Operational Challenges:
• The primary treatment was working at 5 percent efficiency for COD reduction.
• The Biological treatment worked at an average 45% efficiency for COD reduction.
They struggled to effectively treat tough-to-degrade pollutants such as toluene, benzene, Metformin, Acetic Acid, and Methanol which compelled them to run the ETP at 10% less hydraulic load.
A separate stream of higher COD was directed to MEE leading to scaling and fouling in MEE.
The volume of the stream to MEE: 10 KLD
COD: 150000 ppm
TDS: 80000 ppm
Financial Challenges:
1. Urea -DAP consumption: 2160 Kg/month of Urea and 1200 Kg/month of DAP are required to boost the poor biomass in the biological tanks.
2. Electricity consumption: Due to high COD effluent the power requirement went up from a normal 14250 KWH to 20250 KWH monthly.
3. Raw Water Consumption: Due to High COD influence, there was a need for higher evaporation hence around 100000 litres of water was used monthly for MEE.
4. Chemical Consumption: Due to high COD inflow in MEE there was extensive scaling due to which the MEE needed to get cleaned up regularly from Chemicals such as HCL: 22500 kg/month, EDTA: 11250 kg/month.
Extra Costs incurred per month:
| Commodity | Units required |
| Urea(in Biological tank) | 2160 kg/month |
| DAP(in Biological tank) | 1200 kg/month |
| Raw water consumption | 100000 litres/ Month approx |
| HCL (10 % ) | 5500 kg/month |
| EDTA | 3200 kg /month |
| Electricity(MEE) | 20250 KWH/month |
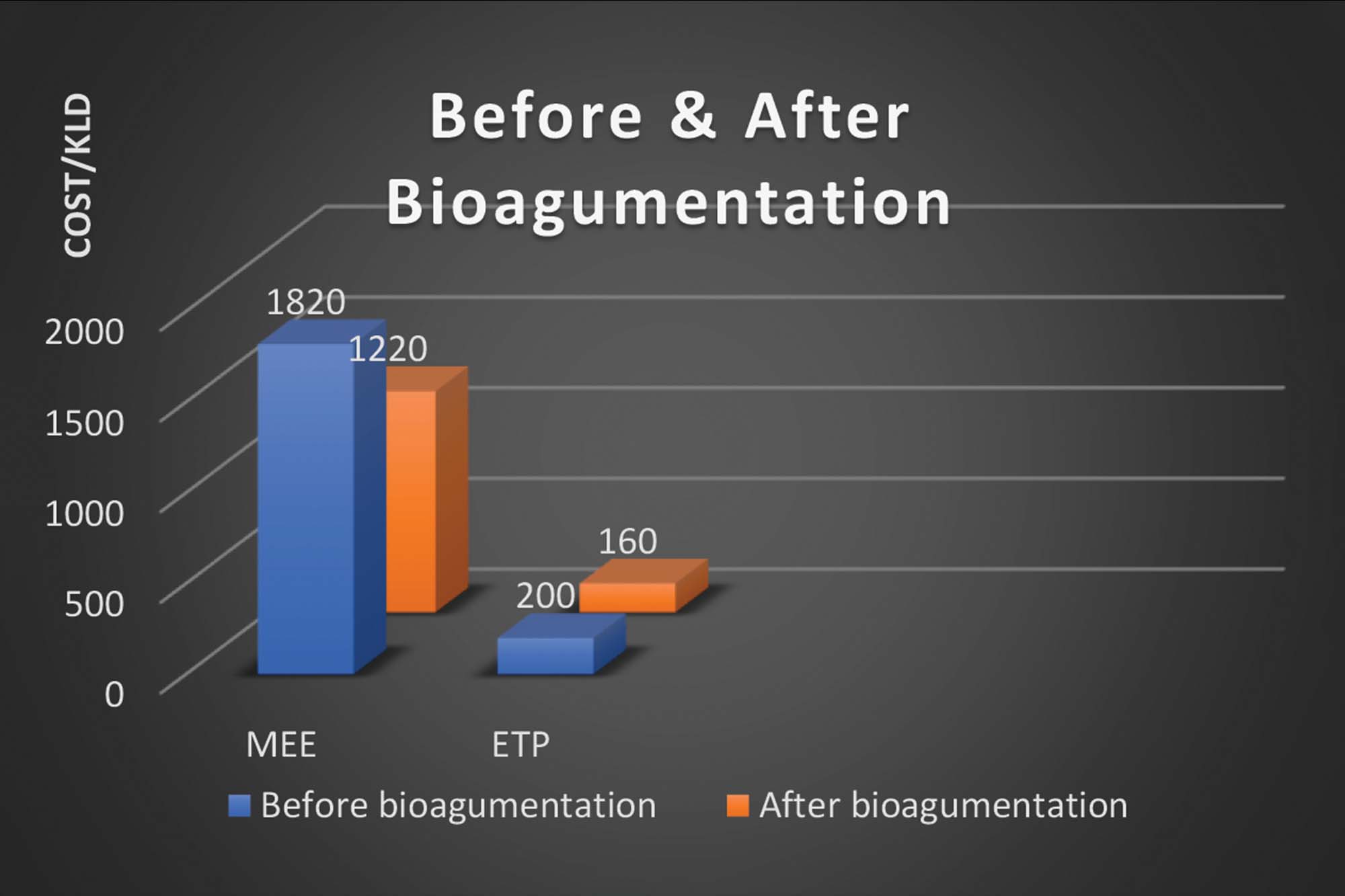
The MEE cost per litre was coming to Rs. 1820/KL for 10 KLD capacity while the overall WWTP cost to treat 450 KLD effluent swelled to Rs. 200/KLD.
The approach:
The industry partnered with Team One Biotech to improve the efficiency of biological units and get rid of the burned-off extra expense they incurred in their WWTP.
Team One Biotech adopted a 3D approach that included:
1. Research/Scrutiny :
• Team One Biotech visited their facility to go through the process of the existing ETP and to scrutinise the pain points and areas of improvement if any.
The visit allowed Team One Biotech to explore potential improvements in the plant, specifically in the biological system and provided a ground for future troubleshooting during the treatment period.
2. Analysis :
• Analysis of the previous 3-month cumulative data of their ETP was done to see trends in the inlet-outlet parameters’ variations and the permutation combinations related to it.
3. Innovation :
• After the research and analysis, Team One Biotech curated customised products and their dosing schedules with a plan of action to get the desired results. This process is called bioaugmentation.
Desired outcomes :
1. Reduction of COD/BOD thereby improving the efficiency of biological tanks.
2. Degradation of tough-to-degrade effluents and develop robust biomass to withstand shock loads.3. Reduction in scaling of MEE by reducing COD in biological systems and saving cost.
4. Reducing consumption of UREA-DAP.
5. Cost saving by treating high COD streams in main ETP.
Execution:
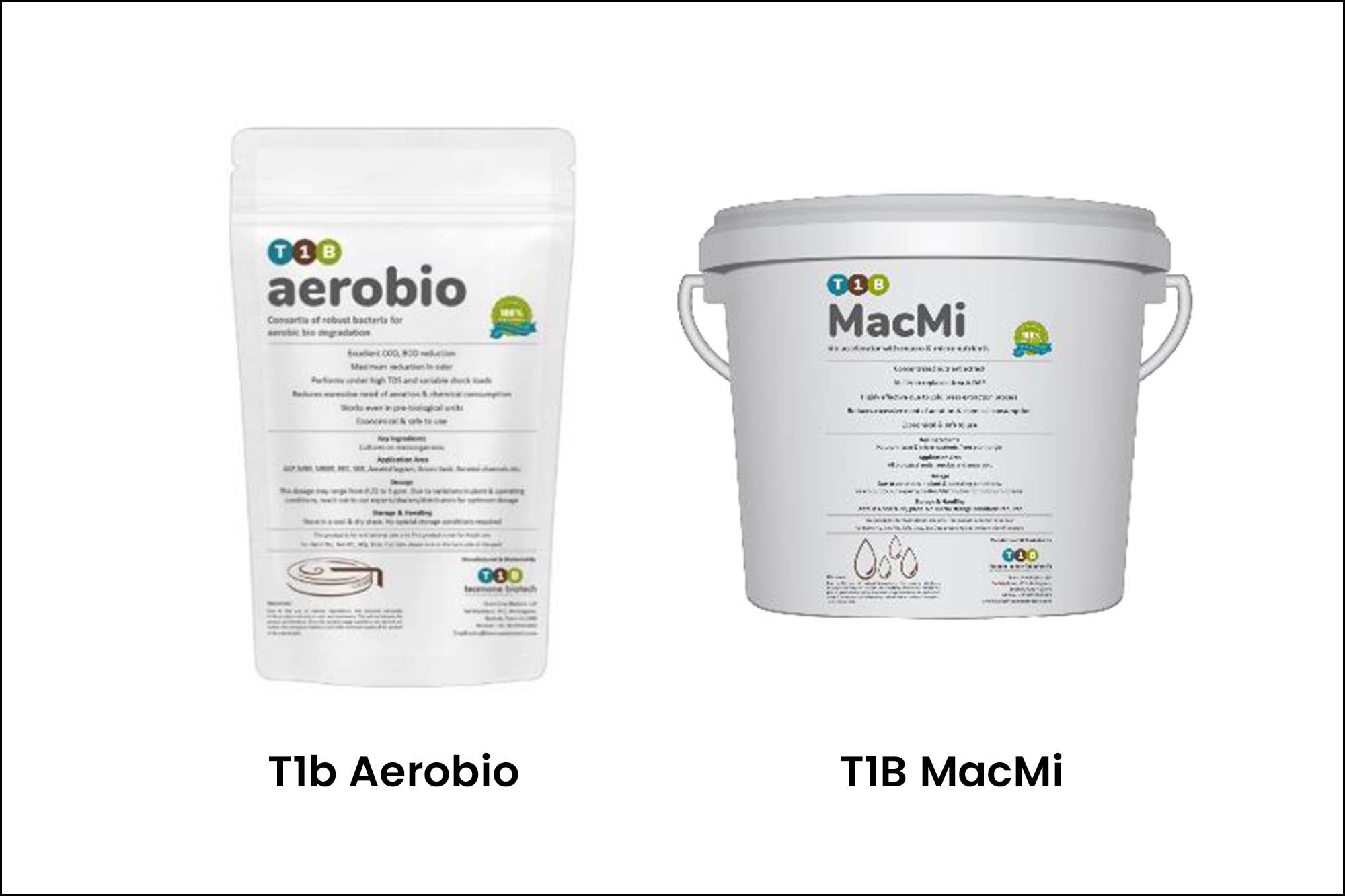
Team One Biotech selected two products:
1. T1B Aerobio: This product consisted of a blend of microbes selected as per analysis secrete enzymes that can degrade tough-to-degrade pollutants such as Toluene and Metformin etc.
Apart from this, T1B Aerobio ensured the reduction of COD/BOD, stability in shock loads, and robust biomass.
2. T1B MacMi: The product was introduced as a replacement for UREA-DAP. It is a plant-based gel that acts as a nutrient source for bacteria consisting of both essential macro and micronutrients.
Plan of action:
1. Diverting 2 KLD of MEE inlet to the main ETP Inlet with COD 150000 ppm.
2. Diverting 3 KLD of MEE reject to main ETP inlet with COD 25000 ppm
3. Dosing of T1B Aerobio in all three biological tanks.
4. Dosing of T1B MacMi in all the three tanks
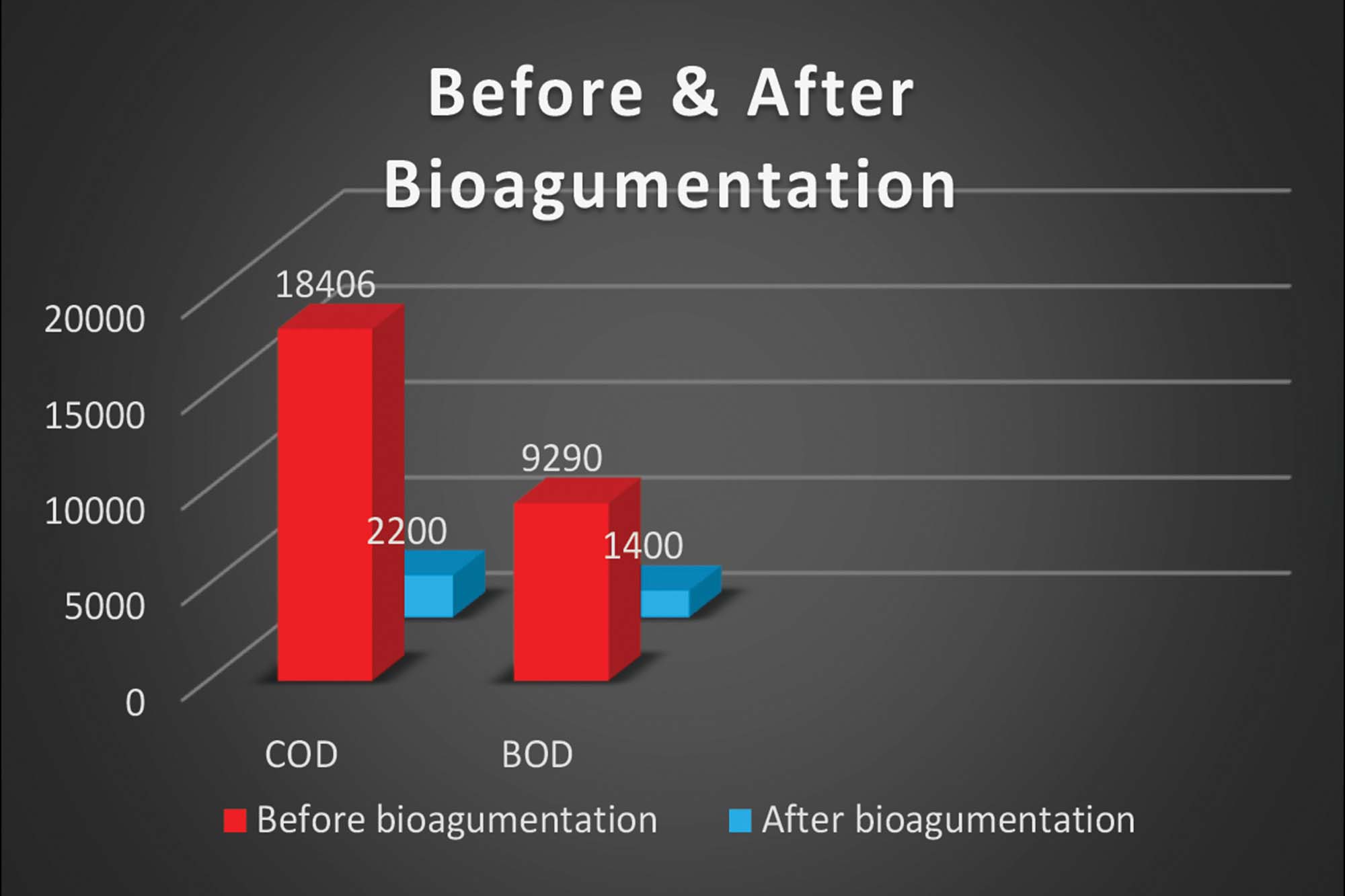
Average Inlet COD after the addition of streams from 2 KLD MEE inlet and 3KLD MEE reject in 450 KLD ETP: 18406 PPM.
Results:
| Parameters | Inlet parameters | Secondary Outlet parameters (ppm) |
| COD | 18406-19000 ppm | 2200 ppm |
| BOD | 9290 to 10000 ppm | 1400 ppm |
Cost Savings:
| Commodity | Units required before treatment | Units required after treatment |
| Urea | 2160 kg/month | 432 kg/month |
| DAP | 1200 kg/month | 240 kg/month |
| Raw water consumption | 100000 litres/ Month approx | 50000 litres/Month |
| HCL (10 % ) | 5500 kg/month | 4000 litres/month |
| EDTA | 3200 kg /month | 2050 litres/month |
| Electricity(Extra) | 675 KWH/day | 478 KWH/day |
With the reduction in commodities used for MEE and wastewater the cost to operate MEE came down to Rs. 1220/KLD and the overall ETP cost was reduced to Rs. 160/KLD.
The implementation of the bioaugmentation program resulted in significant improvements in the performance of biological units in their WWTP:
• The unit achieved around 85% to 89% reduction from their current inlet parameters in COD & BOD.
• The overall ETP OPEX was reduced by 20%.
• The ETP achieved full capacity operations in terms of hydraulic load.
• The biological process became more stable and resilient to fluctuations in the influent characteristics.
• Dependency on MEE to treat high COD effluent reduced. Source: Team One Biotech
www.teamonebiotech.com
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.


















