The AMG-mIoT platform links the manufacturing value chain
By OEM Update Editorial July 11, 2023 6:59 pm IST
This platform aims to enhance traceability and visibility throughout the manufacturing process. By digitising this manufacturing backbone, companies can integrate their critical business processes vertically.
Many manufacturing companies around the world adopt lean methods to enhance their productivity. However, research indicates that 90 percent of these companies need more reliable and detailed real-time data on their machines and processes.
The concept of the industrial Internet, coined by General Electric, refers to integrating sophisticated physical machinery with networked sensors and software. It encompasses various fields such as machine learning, big data, the Internet of Things (IoT), machine-to-machine communication, and cyber-physical systems. The industrial Internet enables the data collection from machines, analyses it in real-time, and utilises the insights gained to make operational adjustments.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communications involve expanding the Internet to include sensors and intelligent connections with physical objects like consumer devices or tangible assets. This connection allows for the exchange of information through the Internet. While the concept and model have existed for some time, there has been a notable increase in the number and variety of connected objects and advancements in technologies for gathering, processing, and sharing information.
The Internet of Things (IoT) market offers a variety of options for combining smart objects and sensor network technologies. Users who employ different communication protocols that are interoperable and diverse recognise the potential of deploying dynamic heterogeneous networks. These networks can be utilised in remote or inaccessible areas such as mines, oil platforms, forests, pipes, and tunnels, as well as in emergencies like earthquakes, floods, fires, or radiation zones. In an IoT infrastructure, these objects or things interact, learn from one another, and share resources, thereby greatly enhancing the range and reliability of their services.
Recently, manufacturing and production environments have been echoing the sentiment of “Wouldn’t it be great if…”. Organisations have long understood the necessity of digital transformation to maintain future competitiveness. However, driven by factors such as the global pandemic, significant challenges in the supply chain, skill gaps, and labour shortages, some companies now realise that more than merely experimenting with technology adoption will be required to compete and survive. We have reached a turning point where smart factory predictions are being made, indicating a shift towards recognising the importance of embracing technology for sustainable success.
From occasional smart factory use cases to full-scale
In the past, the realisation of a fully integrated smart factory equipped with comprehensive solutions has been challenging due to gaps in available offerings and a need for providers capable of meeting all the necessary technological requirements. However, the landscape has evolved as technology has become more affordable, leading to the emergence of numerous start-ups in this field. Previously, advanced technologies and solutions like video analytics, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, autonomous mobile robots, and command centres often required customised and in-house developments. But now, multiple providers offer these technologies and solutions, providing a range of options for each component of the technological puzzle needed to create a smart factory.
Big data will take centre stage
Manufacturers are increasingly embracing big data, which is the foundation of a functioning smart factory. The crucial aspect lies in organisations’ ability to take action based on the data, effectively bridging the gap between technology and human expertise. The convergence of human operators with a centralised command centre holds the potential for genuine business transformation. Every manufacturer needs to evaluate their readiness to adopt smart factory practices. If the answer is negative, a sense of missing out (FOMO) and thorough research on smart factory opportunities can serve as catalysts for initiation, propelling them ahead of the competition.
Cloud and edge computing solutions now offer software explicitly designed for industrial environments. By harnessing the latest IT advancements, these solutions enable real-time utilisation of machine data, whether at the machine level or across global production sites. These enhanced capabilities empower manufacturers to offer customers innovative services and applications globally.
The industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) facilitates the integration of people, products, and processes, enabling digital transformation. Through utilising IIoT platforms, businesses can establish connections, monitor, analyse, and take action based on data in novel ways.
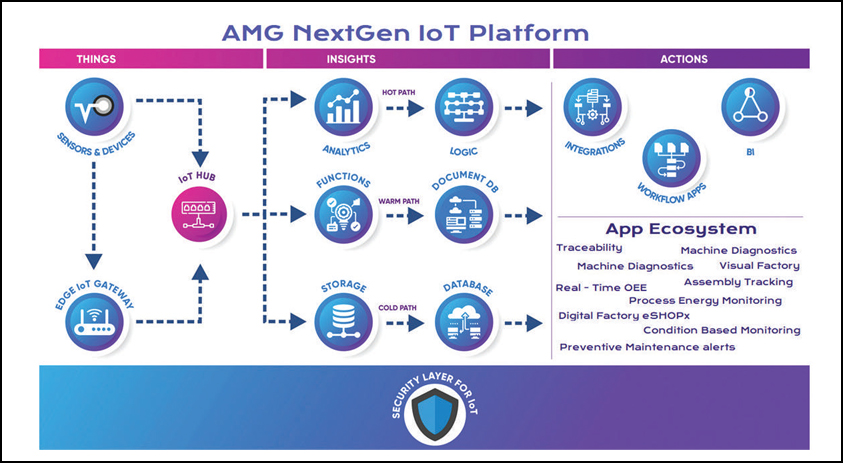
The advanced AMG-mIoT platform is a comprehensive solution that links every aspect of the manufacturing value chain, ranging from the supply of raw materials to outbound processes and everything in between. Its primary objective is to enhance traceability and visibility throughout the manufacturing process. By digitising this manufacturing backbone, companies can achieve “vertical integration” of their critical business processes. Consequently, this integration leads to faster, improved, and cost-effective operations. It enables decentralised decision-making, utilising knowledge-based, predictable, and resilient frameworks.
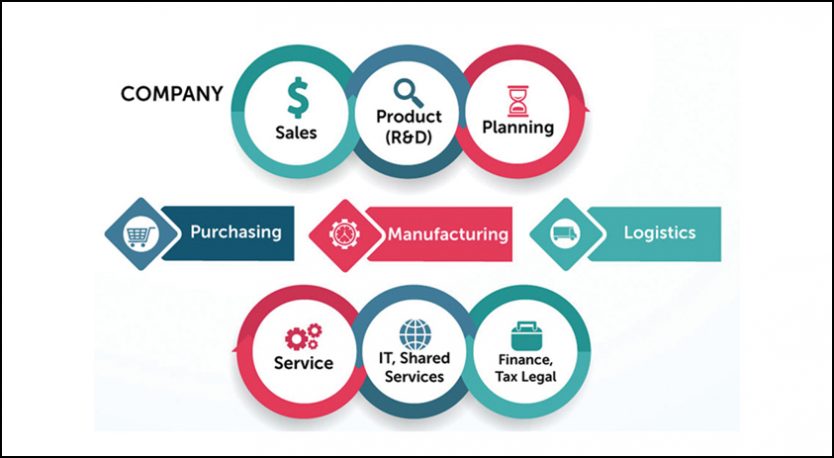
Fig. x: Vertical integration
Such vertically integrated companies may then participate efficiently and effectively in a network of customers and suppliers and tap into global opportunities.
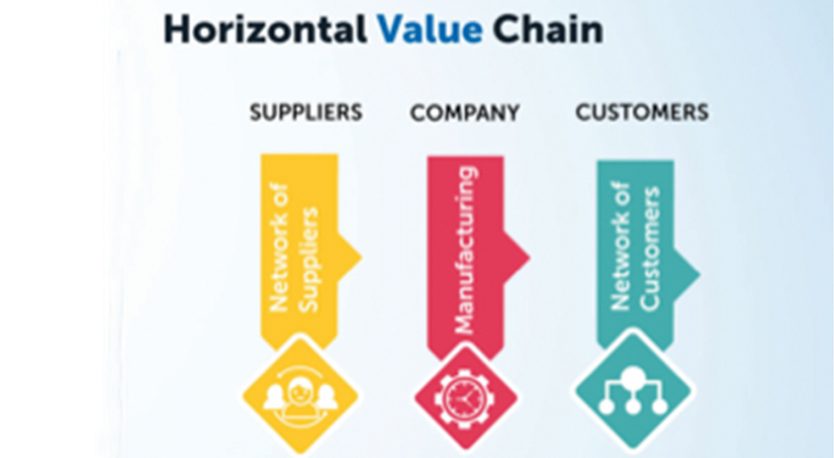
Fig. y: Horizontal integration across the global supply chain
To drive the benefits of Industry 4.0, the AMG-mIoT platform capitalises on a three-way intersection of business processes, smart initiatives, and enabling technologies. This intersection is crucial for identifying desired business outcomes and tangible results. The platform enables autonomous and risk-mitigated operations by providing relevant information, digital workflows, metrics, and key performance indicators (KPIs) to employees. Empowering the workforce with these tools ensures that operations are conducted independently and with reduced potential for adverse outcomes. That is to say, de-risked operations.
AMG-mIoT offers pre-built use cases and applications that deliver a significant return on investment (ROI) for manufacturing companies. These use cases and apps are specifically designed to cater to the unique needs of manufacturing operations such as –
· OEE & Advanced Analytics
· Production analytics
· Process energy monitoring
· Process Parameter – Remote monitoring
· Machine Maintenance Management
· Inspection data management and SPC
· Machine eDocs
· Enterprise workflows: Track & Trace; visual factory; MES & ERP Integration.
AMG-mIoT is an agnostic platform that end-users, machine manufacturers, and service providers can leverage across various industries to enable and deliver outcomes leading to high productivity and profits.
Source: Ace Micromatic Group- mIoT
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.