Tailor-made EOT cranes: Signifying the MHE industry
By OEM Update Editorial August 7, 2019 3:07 pm IST
In an era of evolution, a suitable material handling system can assist in the comprehensive reform of the production activities in the workplace. With an ever advancement in technology, businesses are growing at a rapid rate, hence increasing the total yield of production. It is quite evident that without proper material handling equipment, the pace of the production might hamper causing a drastic effect on the production lines.
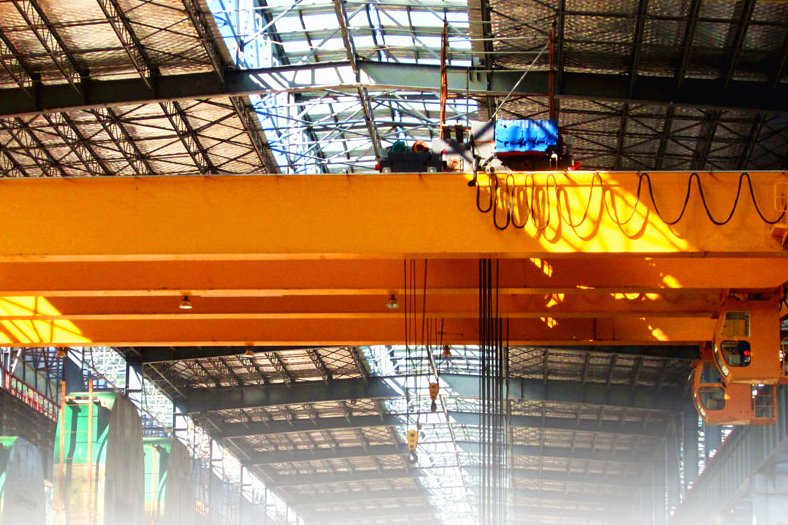
Overhead cranes play a significant role in the segment of workshop material handling equipment. Nowadays, due to the scarcity of labour, manufacturers are moving toward the advancement in types of equipment which in turns attracts a low amount of labourers. However, still in most of the micro and small enterprises, the jobs are performed by the manual labours.
In continuation, in today’s era, the selection of the right kind of equipment is of key importance to effectively upgrade the system and the same can be implied in the case of overhead cranes. E.O.T. Cranes are tailor-made goods, so a standardised product cannot fulfil the needs of the whole industry. There are various factors pertaining to the selection of the speeds and the duty of the crane. To exemplify, the following attributes could be considered while the selection of the speeds of a crane.
• Process
• Material to be handled
• Dimensions of the workplace
• Duty/classification as per relevant Indian standard
Process:
It should be kept in mind while selecting a suitable crane, for what process the equipment should be used. For example, a crane to be installed in the steel melting shop for charging of the material in the furnace, will always have higher speeds than the cranes to be used in the other process involved in the plant. The preferable speeds for the charging crane will be as follows:
• Hoisting speed – 12 metres per minute to 15 metres per minute
• Cross travel speed – 25 metres per minute to 30 meters per minute
• Long travel speed – 60 metres per minute to 80 metres per minute
While the cranes used in the standard workshop or other manufacturing facilities tend to be slower in speeds like:
• Hoisting speed – 03 metres per minute to 05 metres per minute
• Cross travel speed – 15 metres per minute to 20 metres per minute
• Long travel speed – 20 metres per minute to 30 metres per minute
Speeds create an overwhelming space for the purchaser, enabling them to procure the goods at an appropriate price.
Material to be handled:
Material to be handled by the crane will pose a great influence on the sturdiness & speed of the equipment. Some of the processes involved in the industry are highly dependent on the speed of the crane. For example, if the product is not carried from one stage to another in the stipulated time frame, the properties or the outlook of the product might change, damaging the overall product. Seven tank process is an exact example. If the product is not carried in time from one stage to another the whole process would damage the product instead of finishing it. Same can be said in the furnace industry, the ladle handling crane should be designed in accordance with the process to achieve maximum results.
The size of the workplace plays a vital aspect while deciding the speeds of an overhead crane. Bigger the workplace, higher will be the speeds needed. For example, if the length of the workspace is long, a higher speed on long travel will be needed enabling the process to be completed in a successful way. Slower speed can hamper the overall productivity of the manufacturing plant where a high-speed crane is required. Things can change drastically in a vice-versa situation.
Duty/classification of the crane as per relevant standards:
In India IS 3177 and IS 4137 is followed for the manufacturing of the crane. Usually IS 3177 is followed for standard cranes in the industry like workshops, manufacturing shops, assembly shops, etc. and IS 4137 is used for manufacturing of special heavy-duty cranes in the industry like Steel melting shops, Sugar mills, Coal plants, etc. Although the speeds of the crane are not mentioned in relevant Indian standards, the cranes are designed in strict accordance with the speeds desired for the process.
Maintaining high safety, reliability, and precision in the cranes
Safety is treated as the backbone of the material handling industry. Regardless of the capacity of the overhead crane, strict safety procedures are adhered for the manufacturing of the cranes. All the components are dimensionally checked before the final assemblies and fabrications. No tolerances are acceptable under any circumstances. However, various other manufacturers procure material that is available in the open market regardless of the quality, Pioneer Cranes & Elevators (P) Ltd tend to machine their parts on their top quality machinery, and random sample checking is performed across all the stages to produce top-notch quality for their customers. It is evident that following the strict quality control procedures while manufacturing of the equipment will certainly result in the best of the product enhancing the safety and life of the product.
Pioneer Cranes & Elevators (P) Ltd is equipped with the state of the art machinery including VMC, CNC, HMC and various other gears cutting and grinding machinery along with conventional machinery and enabling in timely delivery and producing best of the quality. Availability of the spares also proves a head-on advantage in the safety aspect of the equipment. Suitable spare replacements are readily available which tends to increase the life of the equipment and update functioning of the overhead crane.
Selecting an overhead crane for your application
Appropriate equipment is necessary to get the best out of the application in which it is to be used. Overhead cranes play a crucial role in the working of the industry and if a wrong specification product is selected/procured, it can lead to drastic effects on the overall output of that unit. In a broader view, E.O.T. cranes are classified into four classes as per Indian Standards i.e. IS 3177 and those classifications are as follows:
Although most of the cranes are manufactured as per the above-mentioned standards, there is another standard i.e. IS4137 that covers the special heavy-duty cranes needed for continuous usages, like magnet crane in steel melting shop, cane unloading crane in sugar mill industry and other specified usages. Generally, the process to carry out with the crane creates the outline for the crane manufacturing. To sum up, the following examples of various cranes used in various industries are listed below.
• Maintenance usage – class 2, M5 (medium duty)
• Workshop usage – class 3,M7 (heavy-duty)
• Construction Industry usage – class 3,M7 (Heavy Duty)
• Manufacturing unit usage – class 3, M7 (Heavy duty)
• Steel melting Shop – class 4, M8 (Extra Heavy Duty)
Authored by:
Arshdeep Singh,
Director,
Pioneer Cranes & Elevators (P) Ltd
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.