Technology redefining healthcare withdigital shift
By Staff Report November 5, 2024 7:04 pm IST
Pharma manufacturing has achieved enhanced productivity and quality control in pharma with
Industry 4.0. Automation, data integrity, and seamless integration provide compliance and costeffectiveness, benefiting management, end users, and IT teams with real-time insights.
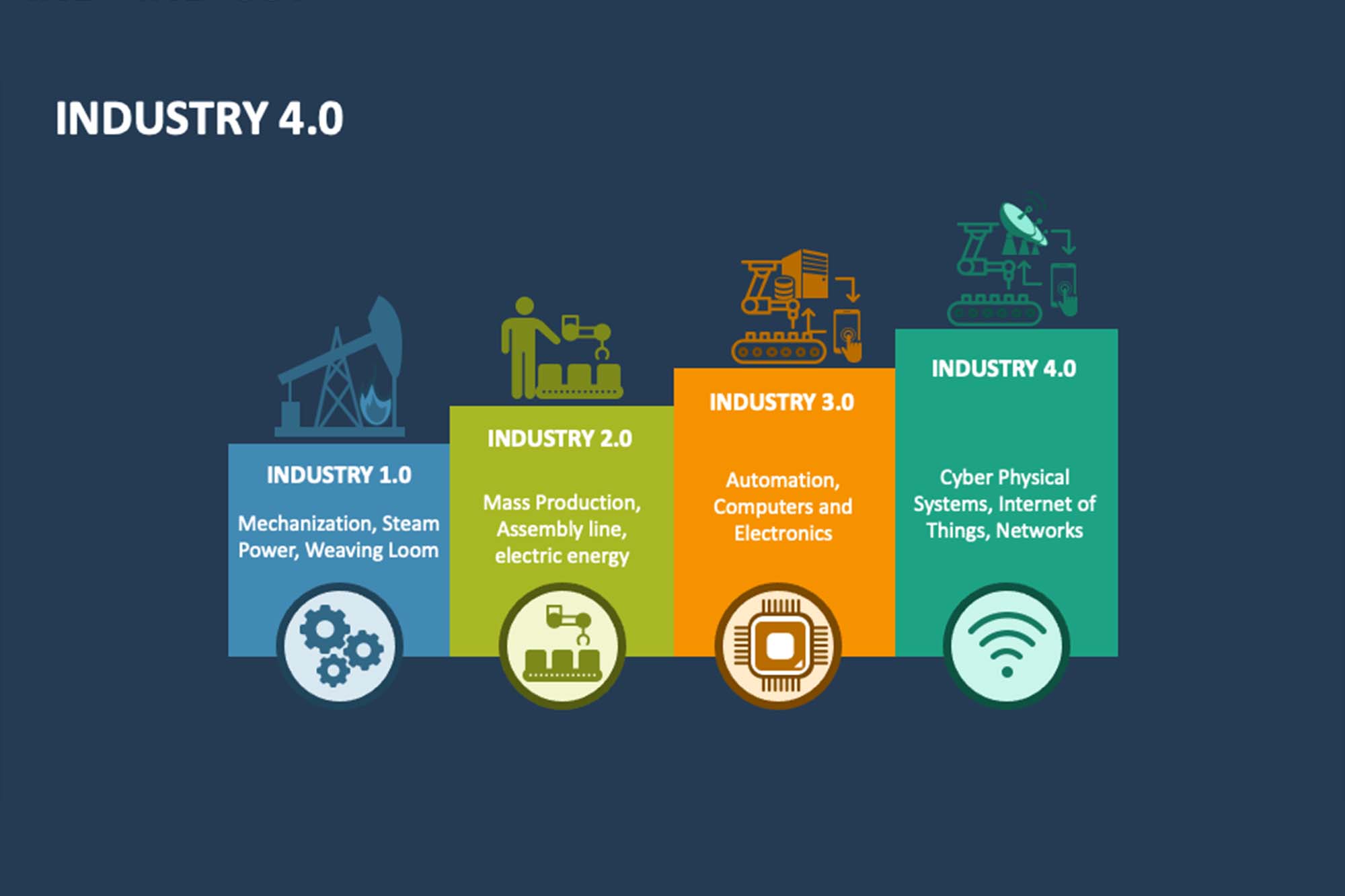
Industrial Revolution from 1.0 to 4.0
The evolution of the Industrial Revolution can be traced through four distinct phases. Industry 1.0 marked the introduction of machinery powered by steam. Industry 2.0 ushered in mass production driven by electricity. Industry 3.0 brought about the use of computers and automation in manufacturing processes. Finally, Industry 4.0, characterised by the internet and cyber-physical systems, changed industries with advanced digital solutions. It was initiated with the Internet and cyber-physical systems. Industry 4.0 technologies have a huge impact on quality manufacturing through digitisation, selfoperating systems, seamless equipment integration, AI, and advancements in computing, leading to more efficient and precise operations in the pharmaceutical sector.
It is a good sign that pharmaceutical manufacturers, regulators, and non-profit organisations like ISPE encourage smart GxP perceptions by applying emerging concepts. Earlier, this was limited to ‘Paper on Glass’; now, it is big data management, data analytics, OEE, IiOT, artificial intelligence, etc.
Enterprise-level systems such as QMS, LMS, DMS, eLogbook and MES are helping pharmaceutical quality manufacturing avoid/overcome data integrity breaches and continuous manufacturing operations.
Productivity and quality compliance
Continual compliance and security: With the advent of Industry 4.0, real-time data generation, reporting, alarms, and audit trails for each transaction are available. We also have access to traceability, including Dispensing to Dispatch, which comprises processes, equipment, environment, and employees.
Design controls: The maximum design controls are through the application; thus, procedural and administrative controls are minimally reliable from the end user’s perspective.
Inherent quality by design: Software solutions embedded with programming tools equipped with prior knowledge, risk assessment, mechanistic models design of experiments, and data analysis assist manufacturers.
Seamless integration: Third-party application integration can fetch and use the required data for further transactions.
Swift deployments: Simplified solution architecture enables adaptability and user-friendliness for superior end-user performance.
Reduced IT dependency: Complex IT infrastructure, such as ON PRIM servers, increases the burden on the pharmaceutical industry, diverting the focus from the core business of manufacturing quality medicine. This can be eliminated by Simplifying IT Infrastructure by availing services through cloud Transactions.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness
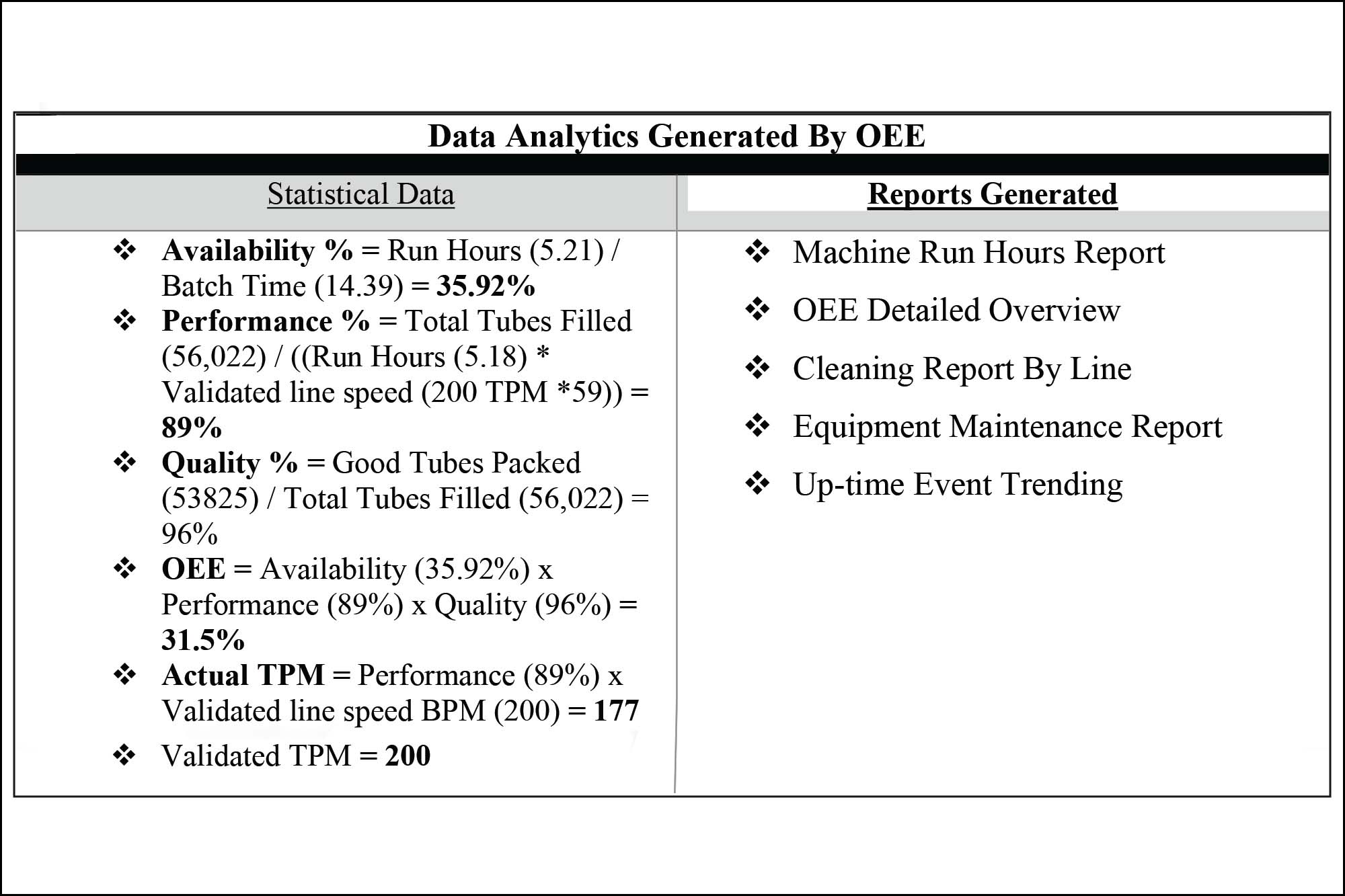
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is an integral part of Industry 4.0 for pharmaceutical manufacturing to measure manufacturing performance indicators.
OEE technology increases the chances of hitting production targets by promoting the visibility of business processes and providing up-to-date information on performance. OEE comes with a percentage score, which decides the ranking.
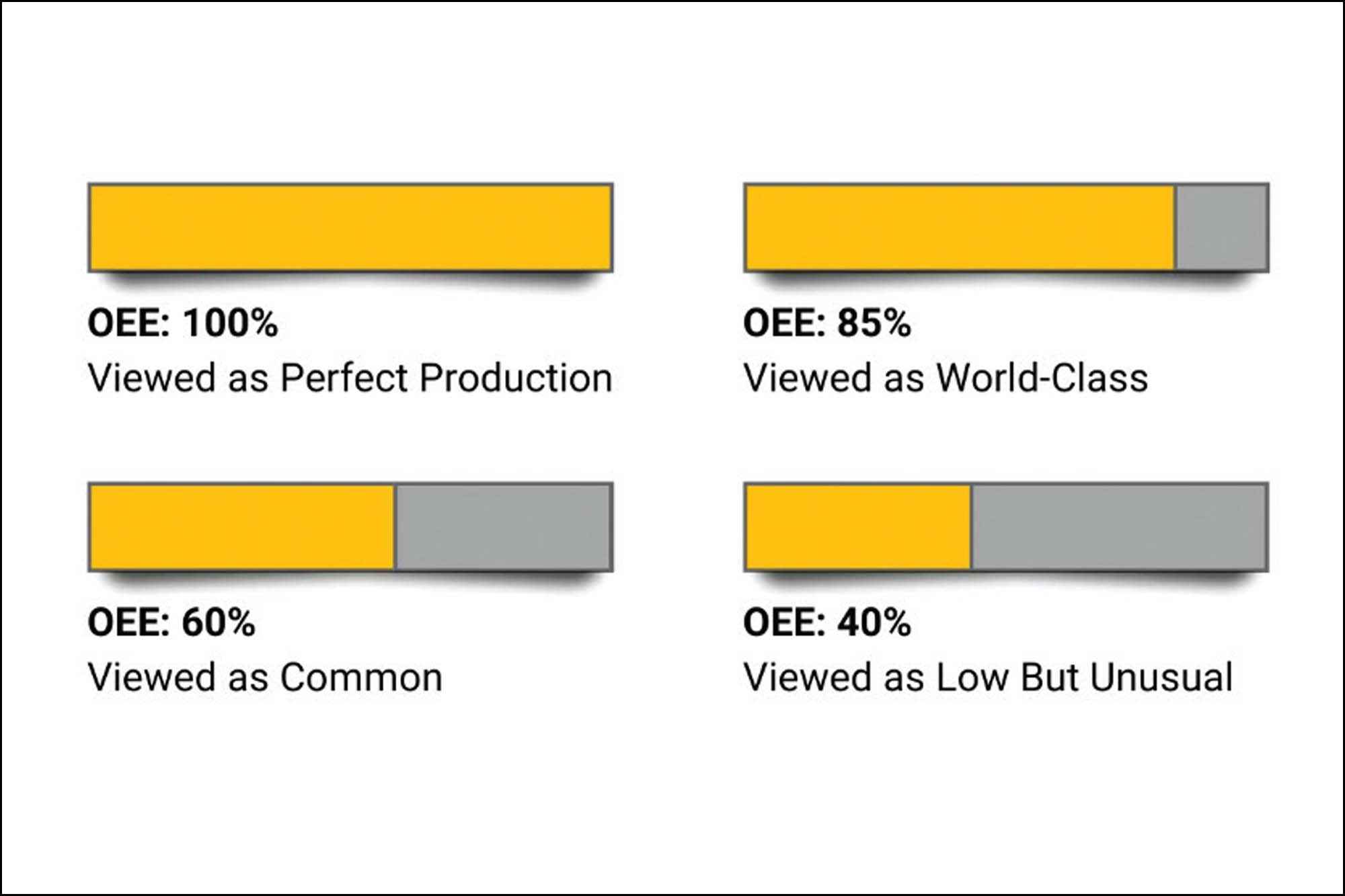
OEE Industry 4.0 helps optimise business processes and maximise efficiency and productivity with available human resources. With advanced metrics demonstrating great detail progress, operations are controlled from a high level to a granular level.
Case Study:
A cosmetic manufacturing company’s OEE helped them pinpoint areas for operational improvement, boosting output and profits while finding hidden capacity.
The secondary packaging line has a Block A Miconazole Cream 10 gm – B. No. PC24001.
Key features of OEE
Real-time alerts in OEE use PLC equipment tags and manual event timers to track line activities. It enhances interface efficiency by leveraging PLC tags to instinctively identify equipment-specific downtime events. OEE collects critical quality attributes (CQA) and critical process parameters (CPP) with product tables to capture key product attributes for comprehensive performance monitoring.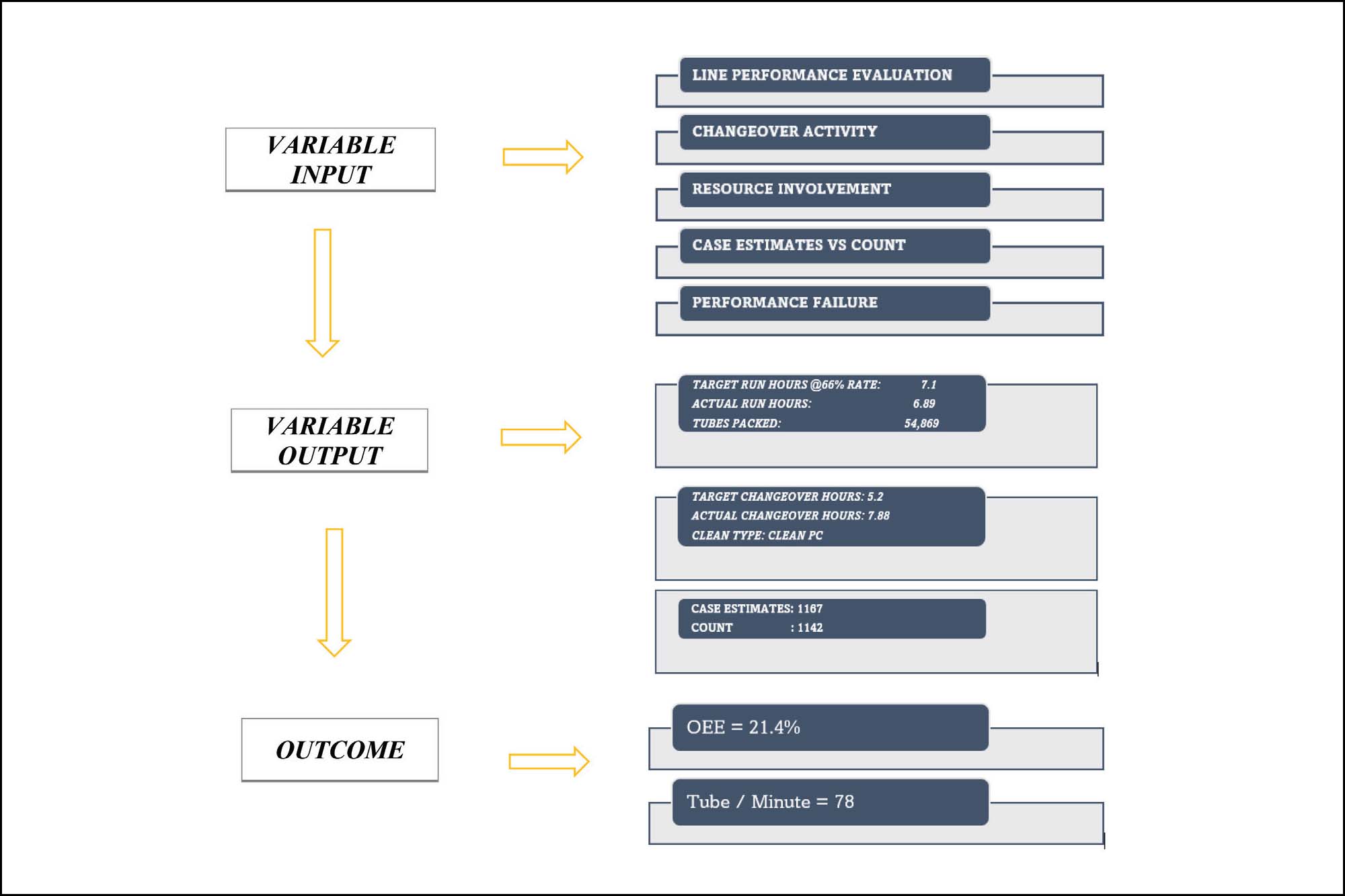
OEE automatically identifies and captures clean times, setup times, equipment repair times, and runtime on each packaging line. It also automatically tracks downtime events through PLC tags for each piece of equipment in the manufacturing and packing area and automatically alerts selected personnel via e-mail in the event of equipment downtime. The OEE system uses a product table to capture target changeover times.
Advancements in pharma manufacturing
A key factor for long-term success with Industry 4.0 technologies is building a selfreliant and well-informed organisation that ensures its Smart GxP approach stays up to date with the evolving business environment.
The entire pharmaceutical manufacturing business model is to develop superior yet cost-effective medicines that are efficient for customers and eliminate delays in the supply chain.
The best way to implement this approach is to adapt Industry 4.0 through practice.
Technology
MES: Control over data integrity and support, along with seamless productivity with design control.
Log: Log activities with electronic recording and complete traceability of supporting events.
eQMS: Digital Quality Functions for the manufacturer.
eLMS: Digitise the training of recruits till the separation.
eDMS: Digitise the creation, review, approval, periodic review, document archival, storage, and issuance activities.
Regulatory Compliance
Industry 4.0 technologies help comply with 21 CFR requirements, FDA audits, validation, and US FDA cGMP requirements. Applications comply with 21 CFR, WHO, EU, and all other major regulatory agencies, which helps establish accountability and traceability throughout the Product Life Cycle.
This is achieved by limiting access to records to authorised individuals, implementing multilayer security protocols to safeguard passwords and login credentials, and ensuring that digital signatures are equivalent to handwritten ones, accompanied by a letter of nonrepudiation. Account sharing between individuals or departments is strictly prohibited, while records are managed through document controls and tracked via an audit trail. Furthermore, signatures cannot be transferred or copied between documents, ensuring the integrity of all records.
Cost-effectiveness
Management Benefit: They can save costs by achieving compliance goals while developing a lean process and gaining real-time, enterprise-wide visibility for better decisionmaking. They can also get behavioural alignment and personal improvement, automated business processes, streamlined operations, and accelerated time to market. Additionally, it enhances visibility into performance, risks, corrective actions, communication, and continuous improvement. Compliance SOPs, efficient operations, and comprehensive training ensure process alignment.
Benefits for End User: The costeffectiveness for the end user is achieved through user-friendly and flexible solutions that enhance efficiency. It reduces manual errors, improves data accuracy, and lowers cycle times, resulting in cost savings through automation. A well-defined work plan with design controls minimises duplication of efforts, further streamlining processes. Overall, these factors contribute to enhanced productivity and optimal resource utilisation.
The information technology team: The team can achieve cost-effectiveness through a cloud server model that reduces the need for extensive hardware infrastructure. It ensures extended business continuity with 99% uptime and provides operational benefits by simplifying maintenance, enhancing scalability, and facilitating seamless upgrades
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.








