Fuel Cell System to boost hydrogen energy at TANAKA production plants
By OEM Update Editorial March 28, 2024 6:45 pm IST
Seeking to cut CO2 emissions at least 50% by 2030 using 500 kW stationary pure hydrogen fuel cell system, which boasts among the largest generating capacities in Japan.
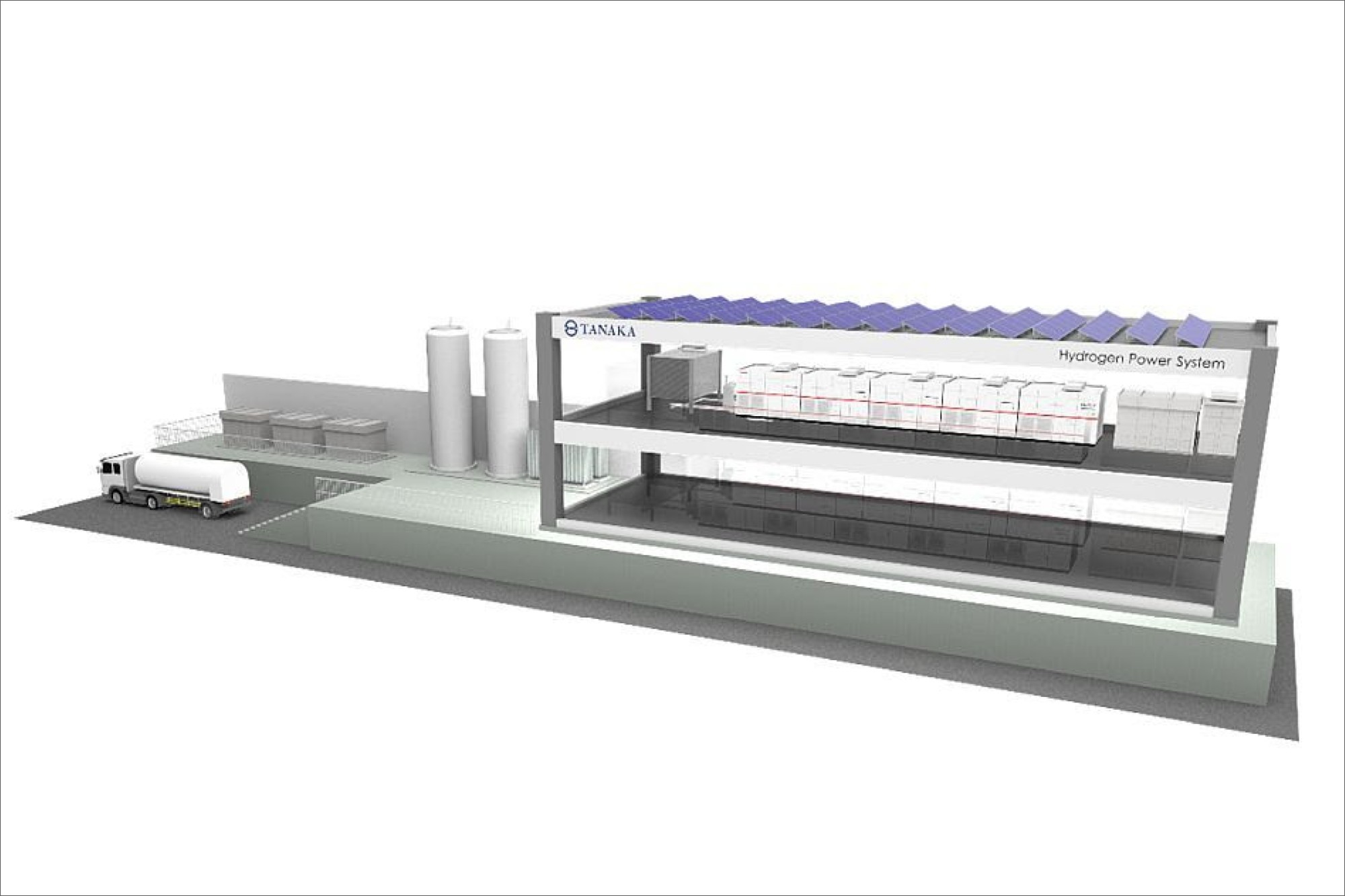
TANAKA Precious Metals will install a stationary pure hydrogen fuel cell system with a maximum generating capacity of 500 kilowatts (kW), one of the largest in private-sector use in Japan, at the Shonan Plant in Kanagawa Prefecture, a key recycling business site for TANAKA. It has decided to install an H2Rex™ pure hydrogen fuel cell system manufactured by Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation to optimally control generating efficiency. Operation is scheduled to commence in 2026.
Initiatives for Achieving Carbon Neutrality
TANAKA is currently carrying out Operation Polaris*2 with the objective of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050. To achieve at least a 50% reduction of CO2 emissions by 2030 (compared to 2013 levels), proactive steps are being taken, including enhancing energy efficiency, optimizing manufacturing processes, implementing green energy solutions, and pursuing additional measures aimed at emission reduction. The recent decision to use hydrogen energy is a part of these efforts.
Pure Hydrogen Fuel Cell Systems
The pure hydrogen fuel cell system to be introduced generates electricity by making use of a chemical reaction that combines hydrogen and oxygen, the reverse of the electrolysis of water. Since the system directly uses hydrogen to generate electricity, unlike household fuel cell systems that extract hydrogen from city gas and other sources, it is able to generate electricity with high efficiency and zero CO2 emissions. Additionally, in the event of a disaster, the system can be used to supply backup electric power without interruption. Such systems also give consideration to the local environment, due to their low noise and vibration.
Effects of Introduction
With the introduction of this system, 25% of the electricity used at the Shonan Plant will be switched to power generated by the fuel cell system, with an expected reduction in CO2 emissions of 1,979 tons annually (this and subsequent figures are estimates by TANAKA). This is equivalent to 32% of the plant’s CO2 emissions reduction target for 2030.
Participation in Councils for Achieving Carbon Neutrality
TANAKA will continue to expand its use of hydrogen energy even after the introduction of the system. In conjunction with this, hydrogen demand will increase, and TANAKA has high hopes for Kawasaki City*3, an advanced hydrogen city in Kanagawa Prefecture, and seeks to build a hydrogen supply base in the waterfront area. TANAKA joined the Kawasaki Carbon Neutral Industrial Complex Formation Promotion Council and the Kawasaki Carbon Neutral Port Formation Promotion Council, two public-private collaborative bodies made up of companies and other organizations in agreement with the city’s vision and strategies that were established to investigate and promote measures for achieving carbon neutrality. By joining the councils, TANAKA hopes to deepen collaboration with the city and other member companies.
Installation Plan and Overview of System
Situated in Hiratsuka City, Kanagawa Prefecture, the TANAKA Kikinzoku Kogyo K.K. Shonan Plant is set to commence operations in April 2026. Representing a significant investment of 2.0 billion yen, this facility underscores the company’s commitment to advancing hydrogen energy technologies.
At the heart of the TANAKA Shonan Plant’s infrastructure lies the H2Rex™ 500 kW pure hydrogen fuel cell system. Manufactured by Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions Corporation, this system comprises five individual 100-kW units. This cutting-edge technology marks a pivotal step forward in promoting the use of clean energy sources within industrial settings.
System FeaturesWith an impressive 95% total efficiency and an estimated durability of approximately 80,000 hours, the fuel cell system at the TANAKA Shonan Plant promises robust performance. Specifically engineered with heavy-duty salt resistance specifications, it is well-suited for installation in environments prone to salt damage, such as port areas.
Moreover, the system boasts an autonomous operating function capable of sustaining operations even in blackout scenarios, ensuring uninterrupted productivity. Complementing this resilience is an advanced Energy Management System (EMS) designed to significantly enhance load-following power generation, offering a fivefold increase in follow-up speed compared to conventional systems.
Specifications
The fuel cell system at the TANAKA Shonan Plant is designed with specific specifications to ensure optimal performance. With a rated output of 500 kW, it operates on a three-phase, three-wire AC system at 210/220 volts. Achieving an impressive total efficiency of 95% based on the low heating value (LHV), this system is engineered to maximize energy utilization. In terms of physical dimensions, each unit measures approximately 2.8 meters in width, 2.0 meters in depth, and 1.9 meters in height, providing a compact yet powerful solution for energy generation.
A Leading Manufacturer of Fuel Cell Electrode Catalysts
TANAKA has been continuously developing electrode catalysts for fuel cells using primarily platinum since the 1980s and currently supplies electrode catalysts for polymer electrolyte fuel cells (PEFC) globally. The FC Catalyst Development Center, located on the grounds of the Shonan Plant, will manufacture and recycle catalysts using hydrogen energy, enabling continuous, stable supplies even during times of disaster. TANAKA will continue further research on precious metal catalysts with the aim of contributing to the widespread adoption of fuel cells and the development of a hydrogen society.
*1: As of March 2024, according to research by Toshiba Energy Systems & Solutions
*2: Operation Polaris is a project carried out per the TANAKA Precious Metals Statement on Carbon Neutrality. With Polaris (the North Star) as a symbol of a fixed guide, the project title incorporates the sense of making steady progress toward achieving its CO2 reduction targets.
*3: Kawasaki City (Kanagawa Prefecture) established the Kawasaki Hydrogen Strategy for the Realization of a Hydrogen Society in 2015 and can be said to be an advanced hydrogen city that has carried out various demonstration projects in cooperation with involved companies.
Council website: https://www.city.kawasaki.jp/590/page/0000139903.html
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.