High-speed machining tool optimises performance for aerospace-grade alloy
By Staff Report August 31, 2024 4:13 pm IST
According to Amit Raina, Country Manager, Dormer Pramet India, selecting the cutting tool geometry and coatings is vital for machining aerospace-grade alloys like titanium and Inconel. Advanced materials and coatings like carbide, TiAlN and DLC address durability, wear resistance, and thermal stability to ensure optimal performance and surface finish.
What factors are vital when selecting milling tools for high-speed machining applications?
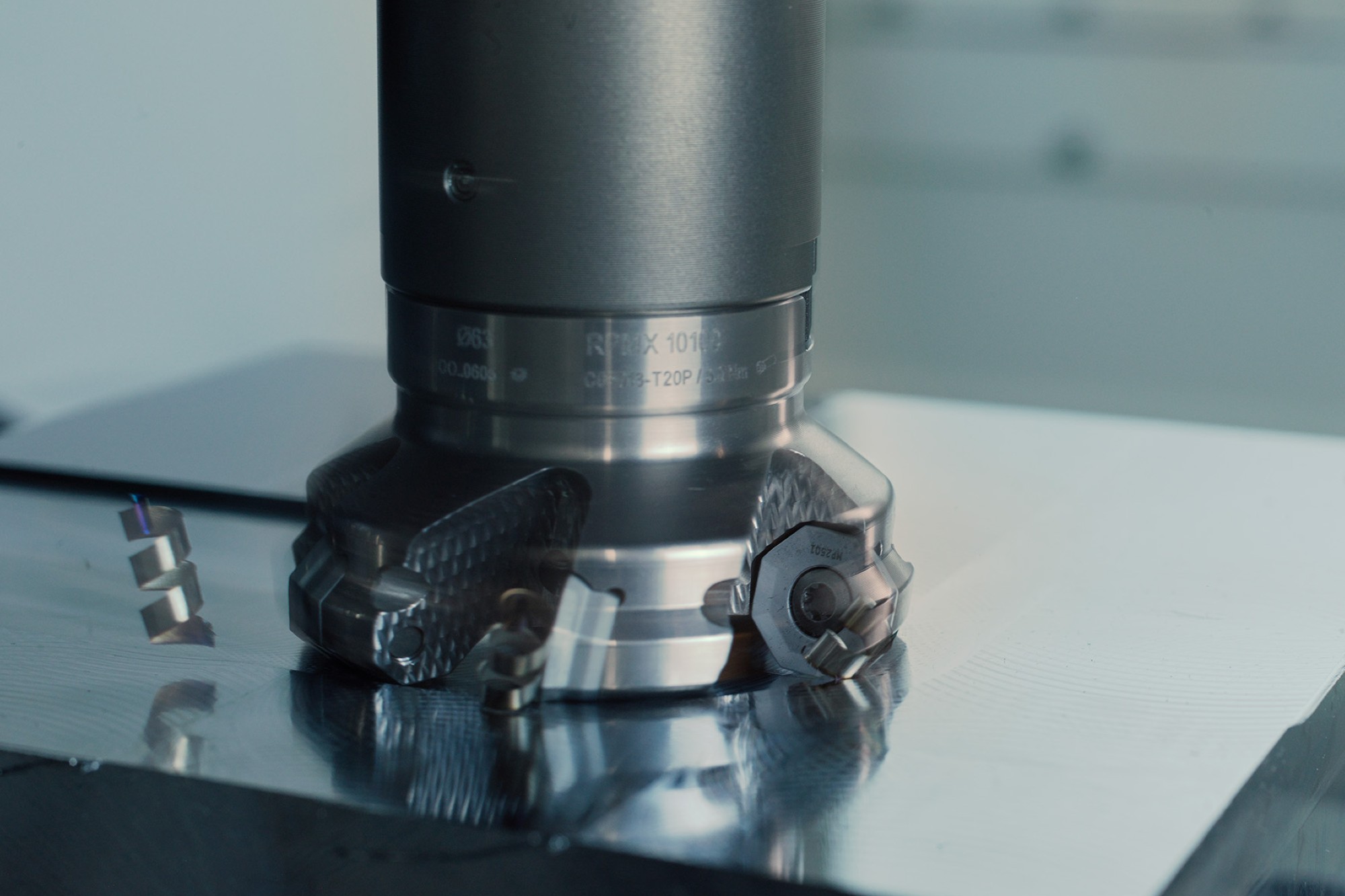
Several factors are considered when selecting milling tools for high-speed machining applications. The tool grade is paramount. It should exhibit high wear resistance to counteract issues like plastic deformation, crater, and flank wear. An ultra-submicron substrate can improve this wear resistance by extending the tool’s life.
A lower approach angle, ideally under 20 degrees, assists chip thinning, allowing for higher feed rates and improved efficiency. Sufficient pocket spaces in the tool facilitate better chip evacuation, while a higher ramp angle improves material removal rates.
The tool geometry should be suitable for the material machined. For instance, HM is ideal for hard materials; MM suits for stainless steel and super alloys. A positive rake angle is crucial as it generates lesser load, and a higher flute count increases material removal rates.
Additionally, larger core diameters add strength to the tool, while differential pitch or variable helix designs are advantageous in reducing harmonics, vibrations, and chattering.
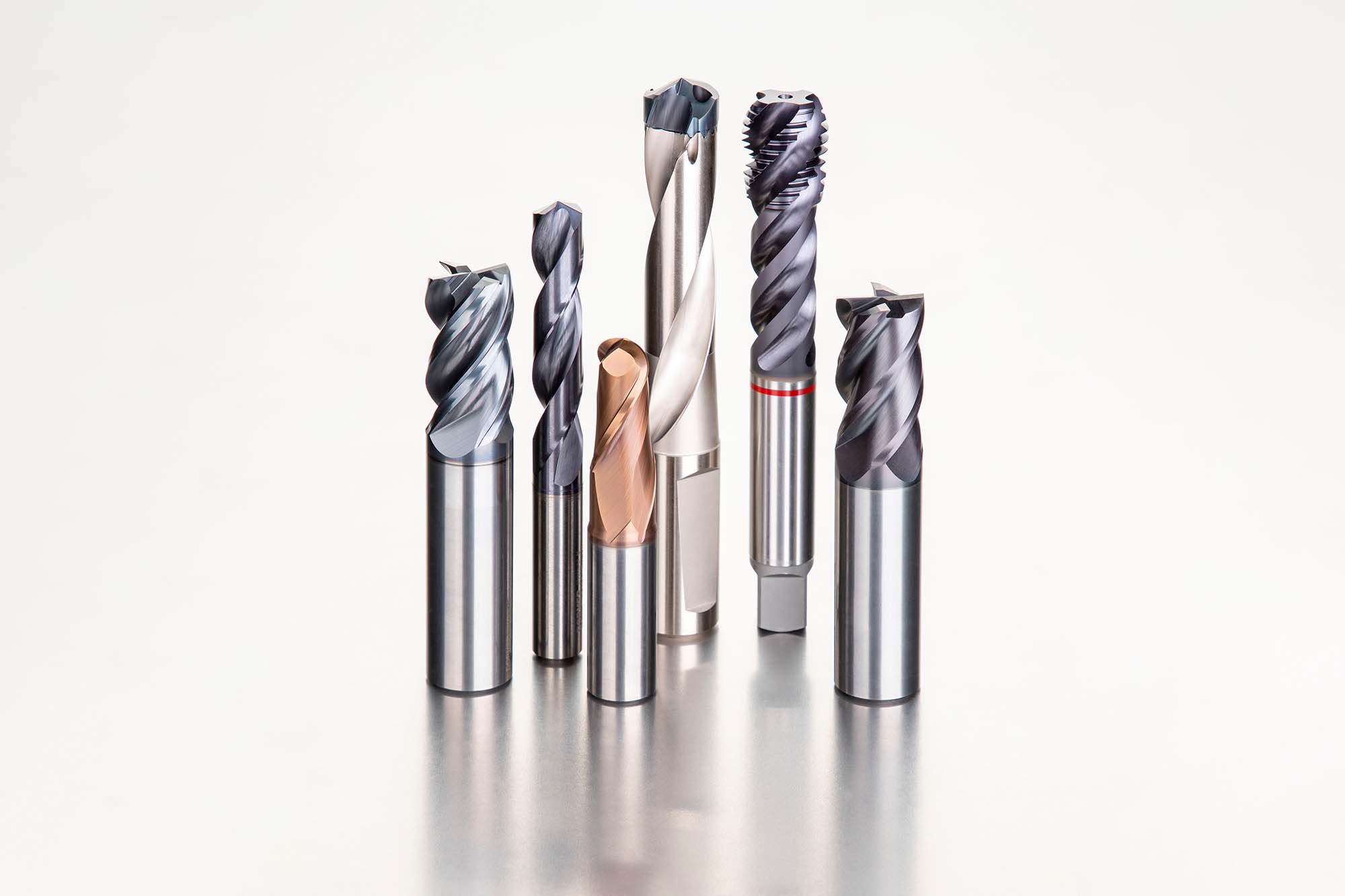

How can the choice of cutting tool geometry impact the surface finish and tool life in milling operations?
The selection of cutting tool geometry is crucial in determining surface finish and tool life during milling operations. Different materials possess different properties and machinability, thus requiring specific geometries to meet machining requirements from roughing to finishing.
For materials like stainless steel and super alloys, a sharp geometry with a high rake angle and optimised edge rounding are essential to avoid burr issues and reduce cutting forces and heat generation. On the contrary, a robust geometry with a larger T-land helps prevent insert chipping for hard materials.
How do your cutting tools address the challenges of machining aerospace-grade alloys such as titanium and Inconel?
Machining aerospace-grade alloys like titanium and Inconel present unique challenges. Tools crafted from carbide, cubic boron nitride (CBN), and ceramics are best for these tough alloys. Advanced coatings such as TiAlN, AlTiN, and diamond-like carbon (DLC) enhance tool performance by providing high thermal stability and reducing wear.
Optimised tool geometries, including variable helix and differential pitch designs, effectively reduce vibrations and improve surface finish. Further, employing coolant and lubrication strategies is essential to managing the high temperatures and stresses encountered in machining these alloys.
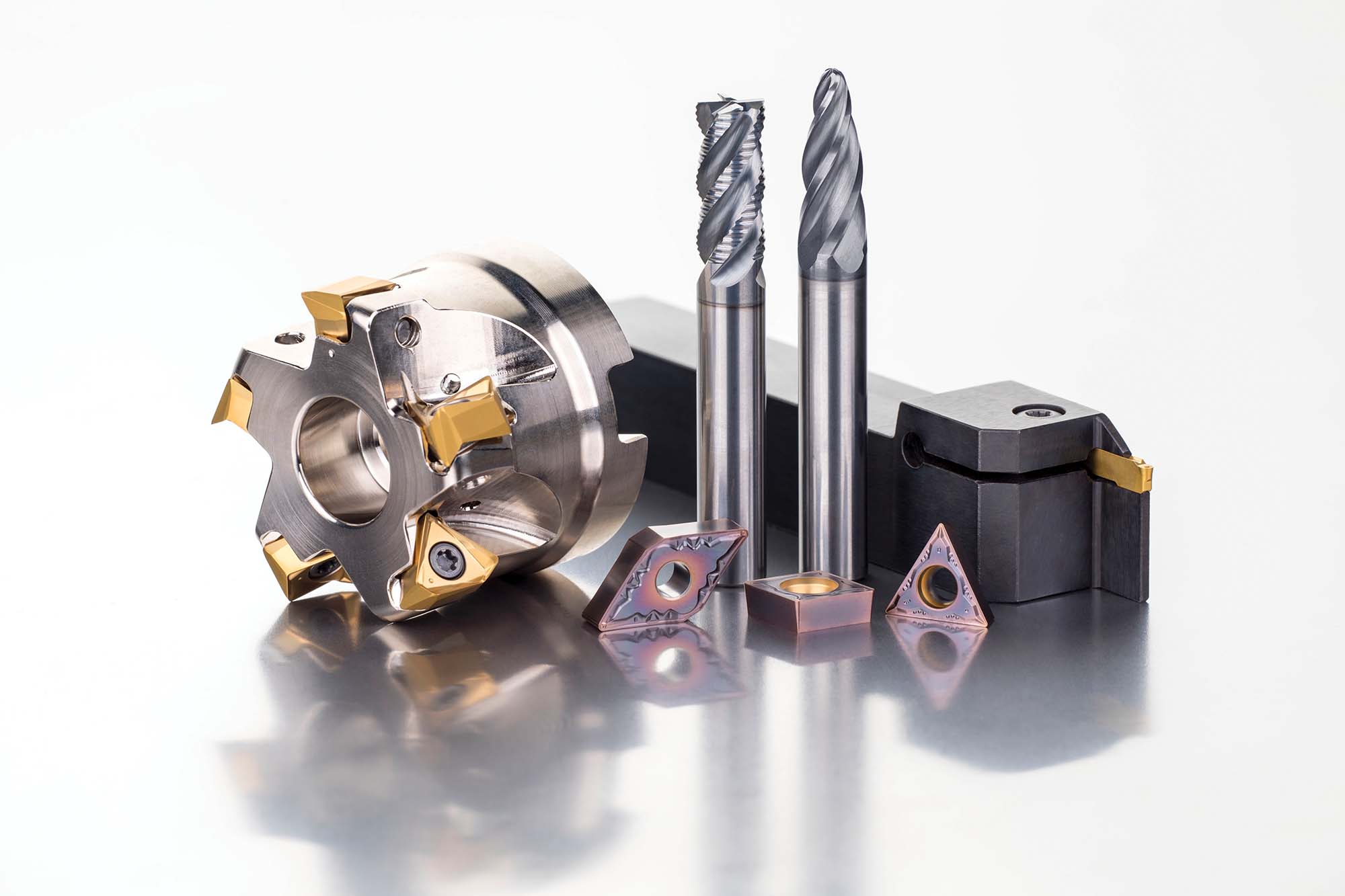

What advanced coating do milling tools utilise in high-temperature machining environments like aerospace manufacturing?
Advanced coatings play a vital role in high-temperature machining environments, such as aerospace manufacturing. Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiAlN) provides superior oxidation resistance and is ideal for high-temperature applications. Similarly, Aluminum Titanium Nitride (AlTiN) is known for its high thermal stability and wear resistance, making it a preferred choice for aerospace applications.
Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings further enhance tool life by reducing friction and wear, which is beneficial in high-speed machining. Overall, PVD coatings are preferred in these scenarios, as a material-specific PVD-grade insert offers high thermal fatigue resistance, e.g., M6330.New generation grades, such as M4310, with proven options like grade 2003, are ultra-sub-micron substrates that offer exceptional performance at high cutting speeds and low feeds in stable cutting conditions. They are particularly suitable for finishing / medium machining operations in challenging workpiece materials.
Moreover, the Solid Carbide end Mill family, like the S2xx, with a rake angle value from 3° to 4°, is best suited for high-alloyed steels >1200 to 1620 N/mm², medium-strength stainless steels >850 N/mm², and medium- to high-strength superalloys>900 N/mm².
Could you elaborate on initiatives taken for Atmanirbharta in the production facility?
Our journey towards Atmanirbharta (self-reliance) and ‘Made in India’ began with the acquisition of Miranda in 2020. This strategic move provided our production unit (PU) with a manufacturing footprint within India. Since then, we have consistently invested in enhancing our production capabilities and capacity.
One significant step was the installation of a new vacuum hardening furnace. This advanced technology improves the quality of our products and contributes to sustainability by optimising energy usage and reducing waste. Additionally, we invested in CNC machines with robot technology to enhance precision, efficiency, and automation in manufacturing processes.
Beyond machinery, we have focused on modernisation, safety, and sustainability. These efforts ensure that our facility aligns with global standards while maintaining a safe working environment for our workforce. It is a matter of pride that our production facility now contributes to the global assortment, with items exported worldwide.
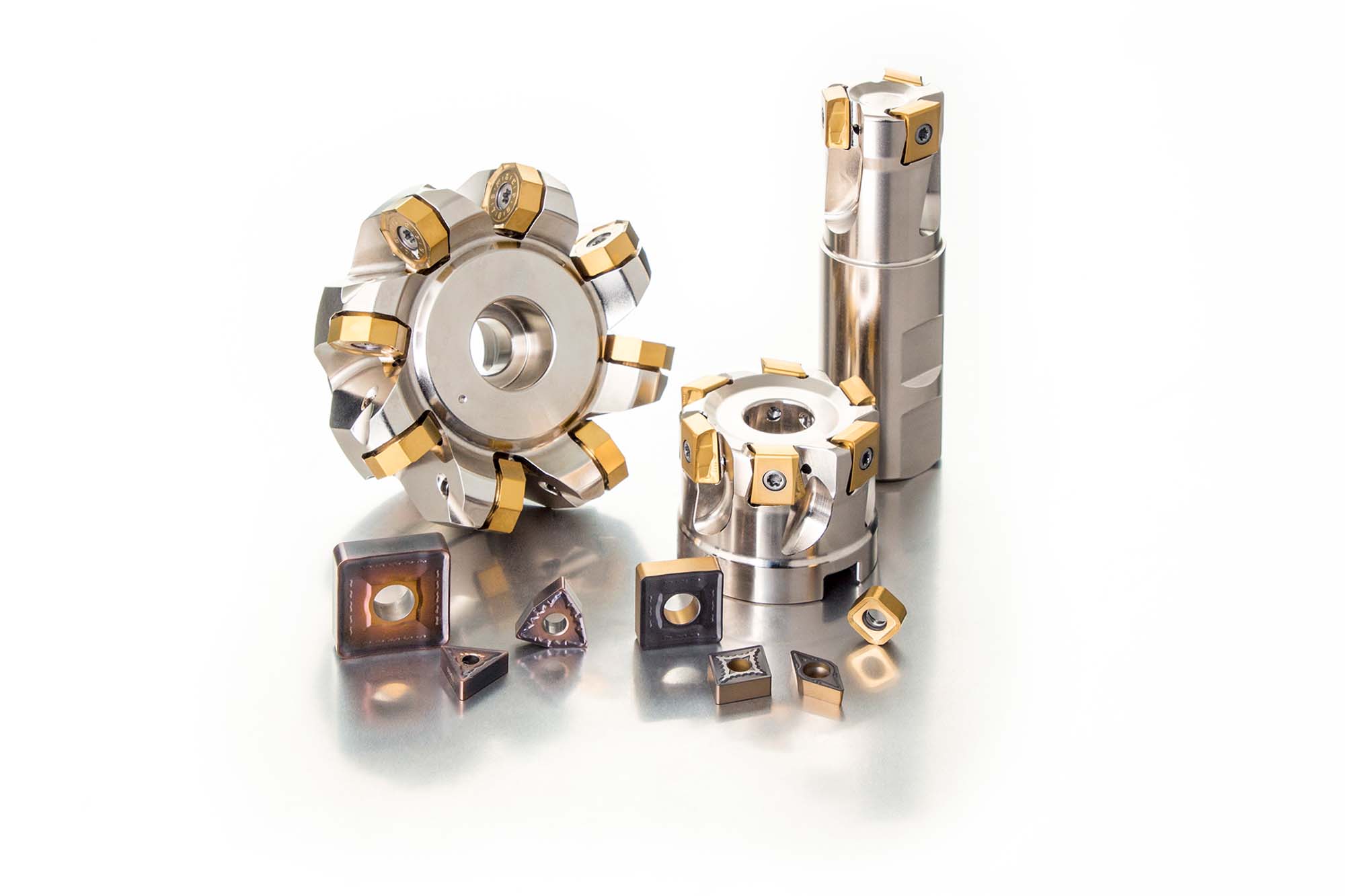

What emerging technologies are shaping the future of machine tools used in the aerospace sector?
Emerging technologies are transforming machine tools and cutting tools in the aerospace sector, driven by the industry’s need for precision, efficiency, and adaptability.
Advanced CNC machining and cutting tools are evolving to deliver tighter tolerances and multifunctionality to reduce production time and minimise errors. Automation and robotics are revolutionising manufacturing by enabling lights-out operations and enhancing productivity through robotic loading and unloading. Machine tools need to be more reliable and consistent to support this shift.
Additive manufacturing is another game changer that allows the creation of complex geometries and rapid prototyping while reducing material waste. It is important to note that the machinability and the tool design should be optimised to machine these challenging profiles.
Smart machining technologies integrating sensors and data analytics are becoming essential for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. These innovations improve productivity, extend tool life and drive the need for tools that integrate with the production setup of machining, inspection, etc. High-speed machining advances are also reducing production times while maintaining high precision. The increased usage of advanced materials to make planes places demands on CNC machines and cutting tools to handle lightweight composites and advanced alloys that are difficult to machine. Multi-axis machining further enhances the ability to produce intricate shapes with high accuracy, reducing the setups required.
These technologies collectively enable the aerospace industry to meet stringent requirements for safety, reliability, and performance.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.