Controlling Pollution in Textile Industry
By OEM Update Editorial November 12, 2016 12:26 pm IST
Pollution has gripped the globe like never before. None of the industries have escaped from causing pollution. We take a look at the pollution caused by the textile industry and the measures that are being taken to control it.
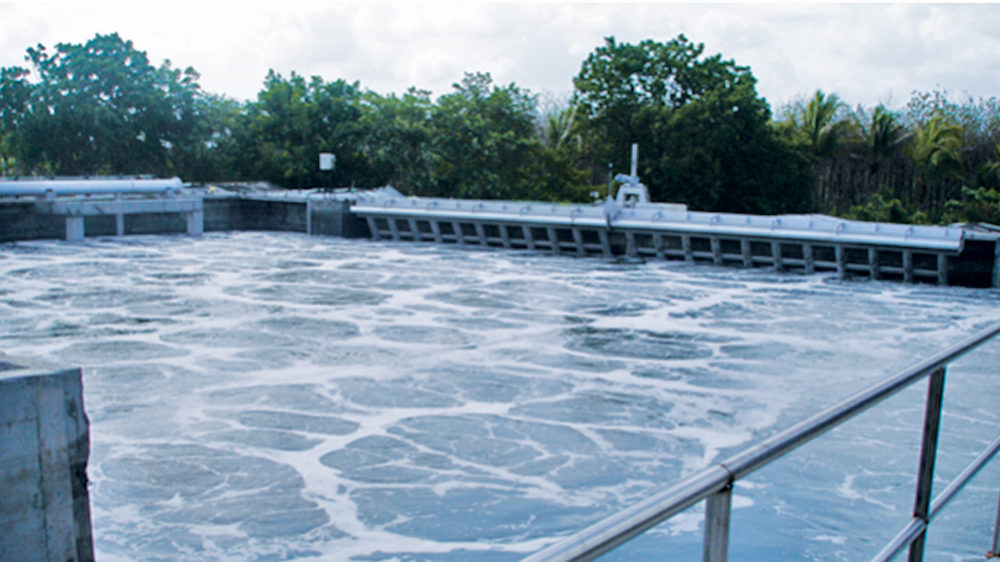
Textile industries are one of the major areas that have an importance throughout the world. However, off recent, the industry has been the epicentre of a massive pollution problem, worldwide. Water pollution is the main issue when it comes to textile industry.
Textile industry is a voracious consumer of water. The water is used for various processes like sizing, scouring, bleaching, dyeing, printing and other finishing processes. In addition to this, the waste water is full of a variety of dyes and chemical additions that add to the challenge that they pose for the environment. This challenge is not only as a waste, but also as chemical composition. Mainly, pollution in the textile waste water comes from the dyeing and finishing processes.
These processes require the input of a wide range of chemicals and dyestuffs, which generally are organic compounds of complex structure. Water plays the role of the principal medium for the application of dyes and other chemicals for the finished touch. As the final product does not contain all the material that is used, the rest turns out to be waste and causes disposal problems.
The growing demands for textile products, mills have resulted in the tremendous rise in pollution as a result of the exponential rise in the problem of pollution in the world.
Speaking about the pollution hazards as far as textile plant is concerned, Satya Narayana Y V V, Director, SFC Environmental Technologies Pvt. Ltd says, “Textile industry is known for consuming large quantities of water. It involves elaborate processing of cloth using variety of chemicals with various wet processes such as sizing, de-sizing, scouring, mercerizing, bleaching, dying, printing and finishing. Based on the market demand and the type of product , the type of process changes frequently which results in variation in characteristics of wastewater continuously. The nature of the waste generated depends on the type of textile facility, the processes and technologies being operated, and also the types of fibers and chemicals used. Each type of wastewater presents a special treatment challenge.”
He further says, “Organic and inorganic substances such as dyes, starches, detergents, salts, toxic organic chemicals, biocides and the ionic metals in textile wastewater causes pollution of receiving water bodies such as rivers and lakes. The wastewater generated from textile industry is usually contains high concentrations of BOD, COD, TDS, alkalinity and colour.”
The chemicals that are used in the textile industry cause environmental and health problems. Among the many chemicals that can be found in textile wastewater, dyes are considered as the worst pollutants. It is observed that the worldwide environmental problems that are associated with the textile industry are typically water pollution caused by the discharge of untreated effluent and those because of use of toxic chemicals especially during processing. The effluent is of critical environmental concern since it drastically decreases oxygen concentration due to the presence of hydrosulphides and blocks the passage of light through water body which is detrimental to the water ecosystem. Textile effluent is a cause of significant amount of environmental degradation and human illnesses. Narayana also says, “If the pollutants present in textile wastewater are disposed without proper treatment, they may cause depletion of dissolved oxygen in receiving bodies causing septic conditions and this affects the survival of aquatic life. High TDS present in the wastewater increases the salinity and the high alkalinity increases the pH of receiving water bodies. Colours from dyes are aesthetically objectionable, particularly in recreational waters. In addition to this, certain carrier chemicals used in dyeing, such as phenol may add taste and odours.
According to Vishal Dethe, Assistant Manager, Organica Biotech Pvt Ltd, the textile manufacturing units generate colossal volumes of effluent rich in chemicals and dyes, generated during the different phases of fabric processing. He says, “The wastewater is laden with pollutants like heavy metals, organo-chlorine based compounds, pigments, polyphosphates, preservatives, formaldehyde, benzidine and azo dyes. These pollutants, along with the solids that are aggregated from the washing processes, increase organic load of water bodies and result in massive fish kills. As they are carcinogenic, toxic and allergic in nature, these harm human beings too. These pollutants account for high COD(Chemical Oxygen Demand), BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand) levels and high volumes of ammonical nitrogen in water reserves. Some textile industries also witness some difficulty in eliminating colour from the effluent.”
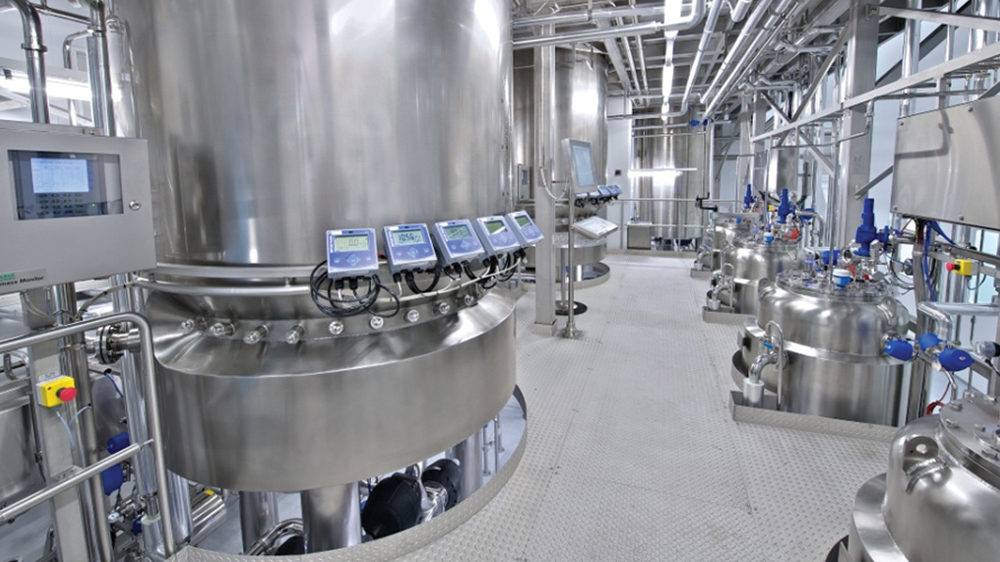
Pollution is a grave issue that all agree to. However, mere discussions on pollution will not help solving the issue. One needs to take some steps in order to reduce the pollution. Speaking about how pollution in the textile industry can be controlled, Dethe said, “Numerous chemical and biological agents are available in the market for optimal waste water treatment. The chemical agents employed for waste water treatment are not only expensive but also cause potential harm to the environment. In contrast to this, several microbial strains can work in an orchestrated manner to facilitate degradation of complex organic wastes in to simple compounds. Some of these microbes can even lead to degradation of recalcitrant compounds. Further, these microbes can lead to reduction of COD, BOD and ammoniacal nitrogen levels of the water reserves. Most of these microbes are conferred with GRAS ( Generally Regarded As Safe ) status and bear no harm to plants, animals or humans.”
When asked how pollution in the textile industry can be controlled, Narayana said, “Reduction of pollution at source is the best strategy to control pollution in textile industry. Reduction in wastewater quantity by adopting water saving equipment, reduction in waste concentration by recovery and reuse of chemicals/ process modification/ etc should be adopted by all textile mills.”
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.