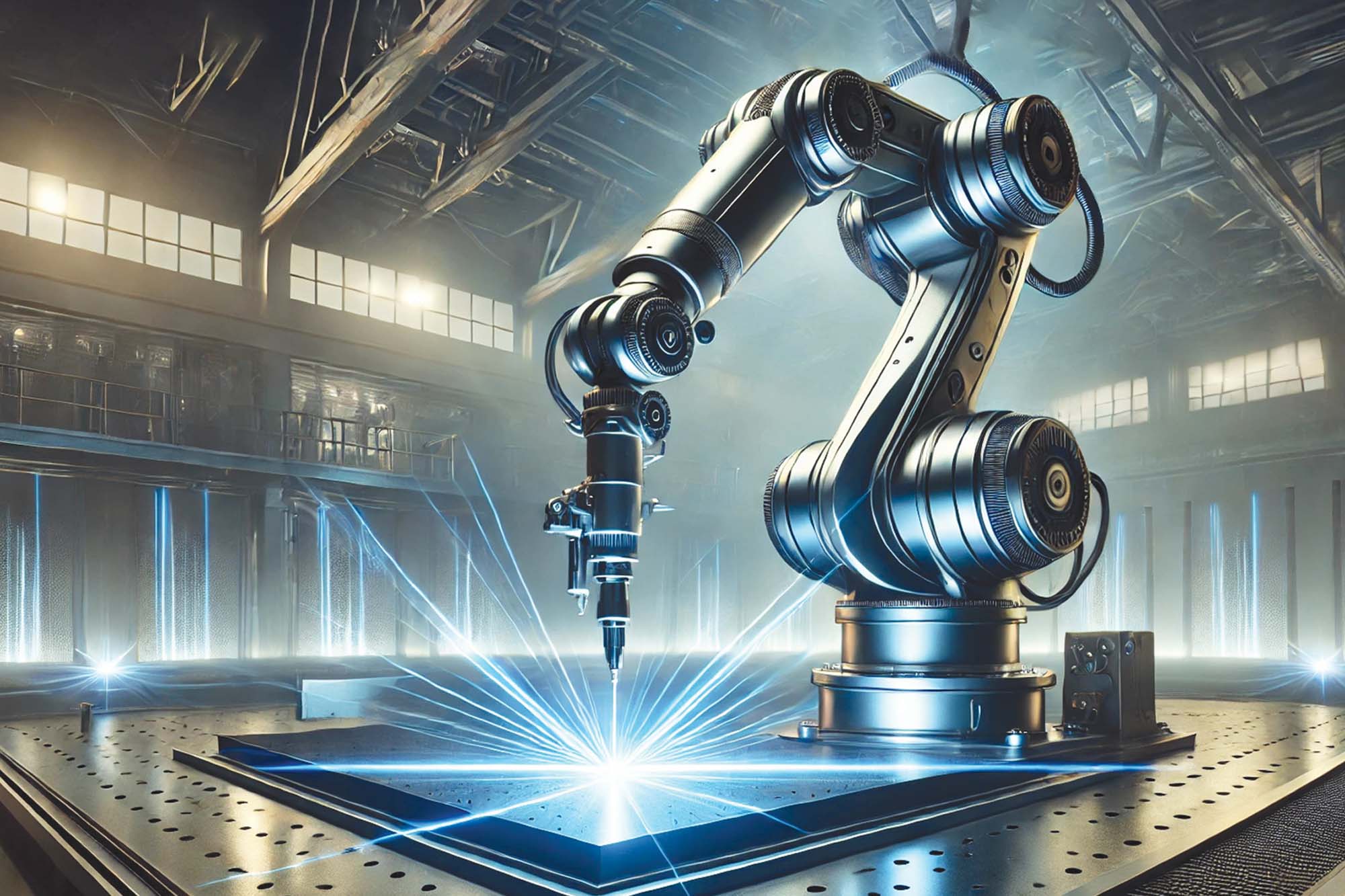
Transformative technologies reshaping welding of the future
By OEM Update Editorial November 1, 2023 12:17 pm IST
In recent years, emerging technologies have begun to reshape the welding landscape, bringing unprecedented precision, efficiency, and safety to this age-old craft. From Laser Beam Welding to Augmented Reality, this story explores the innovative future of joining metals.
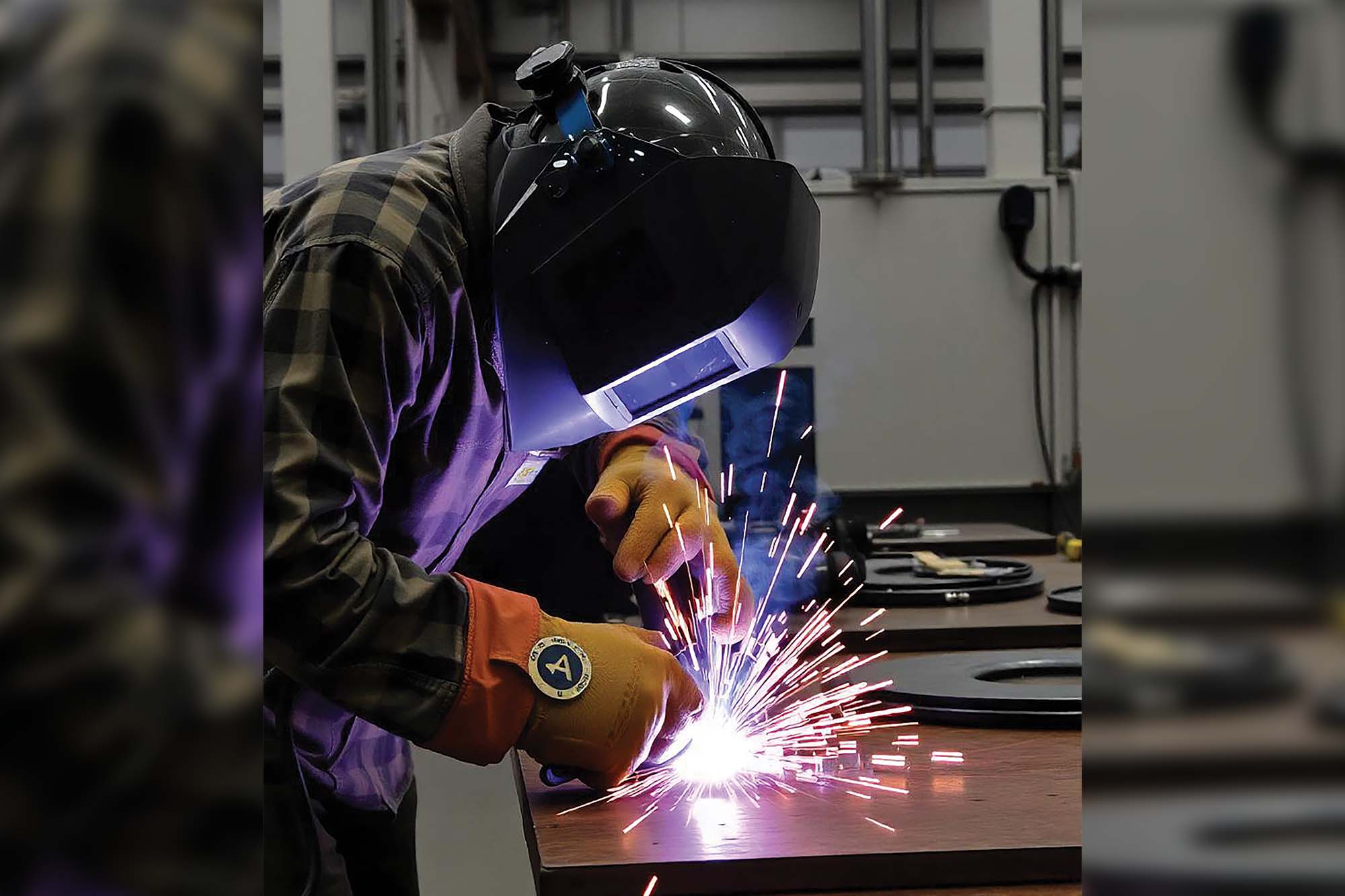
Welding, which combines the art and science of joining metals, has played a vital role in modern industrialisation and infrastructure development for well over a century. From towering skyscrapers to intricate automobile parts, the world we know today has been built with the help of welding. Further, welding technologies have a substantial impact on pharmaceutical manufacturing, with current advancements focusing on using advanced welding materials to achieve precise, contamination-free connections. The welding and cutting sector is poised for significant expansion, primarily due to India’s heightened focus on infrastructure advancement. India’s infrastructure initiatives drive a growing need for welding and cutting services across various industries. Notably, infrastructure development emphasises projects like road construction, bridge building, and architectural construction, all of which require welding skills to ensure structural durability and integrity.
Nimesh Chinoy, Director of Sales & Marketing at SigmaWeld, emphasises that productivity and data analysis are the key drivers behind the transformative impact of welding technologies on the manufacturing industry. Technological innovations, from augmented reality welding to laser beam welding in space, are poised to revolutionise the industry, contributing to broader automation trends, sustainability, and globalisation. One of the innovative welding technologies making waves in the manufacturing industry is Laser Beam Welding (LBW). This method harnesses a powerful laser to create a focused beam of light, which is used to melt and join metals.
A novel trend in welding equipment involves the capability to retrieve Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) data from a server, recognise the welder, and automatically configure the equipment to operate within the specified current and voltage range. Another noteworthy trend is Hybrid Welding, which integrates various welding techniques, such as laser welding, Gas Tungsten Arc Welding, or MIG welding. By combining the strengths of these methods and mitigating their weaknesses, hybrid welding establishes a precise and stable welding process. The use of automation, robotics, and data analytics is further reshaping the welding landscape, reducing the reliance on manual labour and improving the quality and sustainability of welding processes.
Automation and robotics: the rise of welding machines
Automation and robotics are on the rise in the welding industry. The integration of welding automation and robotics is improving efficiency and safety within the sector. The sector is undergoing significant changes due to the influence of Industry 4.0, which includes the growing adoption of automation and robotics, as well as the utilisation of data analytics to enhance future welding processes. The manufacturing industry is increasingly turning to automation, robots, and collaborative robots due to the need for more skilled workforce. Automation is increasingly being integrated into welding processes, enhancing productivity and ensuring consistent weld quality, which is crucial for industrial applications.
While automation handles repetitive tasks, there is a growing need in the industry for highly skilled welders who can proficiently manage complex machinery and ensure optimal performance. Automation and robotics are playing an increasingly significant role in the welding industry. These machines can operate continuously, reducing the need for human welders to perform monotonous, physically demanding work.
Dr. T.J. Prasadarao, Executive Director (Technical) at D&H Sécheron, highlights the importance of remote robotic welding, especially in hazardous or sterile environments within the pharmaceutical sector. Robots can work with precision and without risks to human workers. Robotic welding arms, equipped with sensors and adaptive control systems, can seamlessly adjust to variations in materials and joint configurations, ensuring consistently high-quality welds. These robots are also more resistant to the physical strains of manual welding, making them ideal for tasks in challenging environments such as offshore oil platforms or nuclear facilities.
Furthermore, automation is contributing to a more sustainable welding industry. Robotic welders are programmed to optimise material use and minimise waste, a crucial factor in the context of growing environmental concerns. As we strive to reduce the carbon footprint of manufacturing, automation offers an elegant solution to minimise resource consumption while maintaining high-quality standards. Furthermore, augmented reality welding is one of the most exciting developments in welding technology.
Emerging welding technologies
Emerging welding technologies represent the forefront of innovation in the manufacturing sector. The initial preparation of metal for welding frequently involves cutting, fitting, and beveling the base material, mentions Ravichandran Duriaswamy, AGM- Product management, Messer Cutting Systems India. The meticulousness and care invested in the initial cut can significantly reduce the need for extensive post-processing. These state-of-the-art techniques and methodologies are meticulously crafted to elevate precision, efficiency, and safety throughout the welding process.
From the integration of augmented reality to the adoption of Laser Beam Welding (LBW) and Friction Stir Welding (FSW), and the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) into welding practices, these breakthroughs are driving a transformation in industries such as aerospace and pharmaceuticals. Irrespective of the application, effective metal preparation for welding remains paramount for delivering top-notch results, sustaining consistent productivity levels, and curtailing expenses, particularly those linked to rework and downtime. As technology continues to evolve, these emerging welding technologies promise to drive excellence in welding practices.
Augmented reality welding
Augmented reality welding systems have the potential to revolutionise the way welders work, making their jobs safer, more precise, and more efficient. The introduction of AR welding helmets, equipped with sensors and cameras, provides welders with real-time data and visual overlays that enhance their abilities. These smart helmets can display critical information, such as weld parameters, joint alignment, and work instructions, directly in the welder’s line of sight. Moreover, AR welding systems also assist in training new welders. By simulating welding scenarios in a virtual environment, apprentices can practice their skills without the risk of damage or injury.
Laser beam welding: precision beyond measure
Laser beam welding (LBW) is another emerging technology, making it suitable for applications where exacting tolerances are required. One of the key advantages of LBW is its ability to weld thin materials without distortion. This is particularly valuable in industries like electronics and medical devices, where delicate components must be joined without compromising their integrity. Additionally, the heat-affected zone in LBW is minimal, reducing the risk of thermal stress and distortion in the welded materials. LBW, excelling in joining dissimilar materials, opens up new possibilities for lightweight and high-performance material combinations in various applications.
Friction Stir welding: a new dimension in joining
Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is another notable advancement in welding technology. Its exceptional strength and precision make it an excellent choice for welding pharmaceutical machinery, ensuring durability and reliability in the equipment. FSW is a groundbreaking joining process quickly gaining traction in various industries. Creating a strong and defect-free bond, this process is particularly useful for joining dissimilar materials, which is often a significant challenge in traditional welding.
FSW offers several advantages, such as reduced distortion, improved fatigue properties, and enhanced corrosion resistance. It’s an ideal choice for industries like aerospace, where lightweight materials like aluminium and composites must be joined without compromising structural integrity. Furthermore, FSW generates significantly less heat, creating a safer working environment. Friction stir welding has found its way into space missions, where its ability to create robust and precise welds in zero-gravity environments is invaluable. As humanity continues to explore the cosmos, FSW will play an integral role in constructing spacecraft and habitats for future space travellers.
Nanotechnology and welding in space
Nanotechnology is reshaping the future of materials science and engineering, and welding is no exception. Researchers are exploring the integration of nanomaterials into welding processes, opening up new possibilities for enhanced weld properties. Nanoparticles can be added to welding materials to improve their strength, durability, and resistance to environmental factors. For example, adding carbon nanotubes or graphene to welding filler materials can create super-strong welds that are also highly corrosion-resistant.
Industry 4.0 and skilled welders
The welding industry is undergoing its own Industry 4.0 transformation, integrating digital technologies, automation, and data-driven decision-making into manufacturing processes. The worldwide demand for proficient welders is steadily rising, especially with the thriving manufacturing sector. Automation is a key factor in enhancing welders’ capabilities to transition into operator roles. Nevertheless, a strong fundamental understanding of welding remains essential for operating automation. Vishwanath Kamath, Managing Director, Fronius India, underscores that the increasing need for welding services is creating a call for skilled welders and specialists in robotic welding, offering employment opportunities and avenues for career advancement. The demand for skilled welders is steadily growing globally, particularly as the manufacturing sector thrives. Automation plays a significant role in elevating welders’ skills to become operators. However, having a solid foundation in welding knowledge remains a prerequisite for operating automation.
The need for proficient welders will remain constant, even with automation and advanced welding techniques. Instead of focusing solely on improving welders’ general manual welding skills, customised welding training programs are designed to address the precise requirements of individual welders or specific organisations. These programs aim to transform participants into experts in their field. Welding cobots or collaborative welding robots are designed to complement human welders during the welding process. The economic viability of implementing robotic welding systems, including cobots, versus manual welding operations depends on various factors, primarily production volume, labour costs, and quality requirements. Government-sponsored skill development and vocational training programmes, such as the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), aim to improve employability by providing extensive welding training.
Welding technologies for modern industry
Modern welding is firmly rooted in cutting-edge materials and techniques, serving as the cornerstone of innovation in various industries. Specialised welding methods are crucial for accommodating high-strength alloys, exotic metals, and composite materials, ensuring the longevity and performance of welded structures. Sustainable welding practices and consumables play a vital role in reducing the environmental impact of contemporary manufacturing while upholding stringent production standards.
Furthermore, utilising specialised consumables with characteristics such as minimal carbon and remarkably low sulfur content has become instrumental in minimising the risk of contamination. Techniques like orbital welding and laser welding are gaining prominence due to their precision and the absence of impurities, particularly in critical applications. In the realm of welding small pharmaceutical components and devices, Microjoining with Laser Welding has gained significant importance owing to its precision and suitability for these specialised tasks. The overarching goal is to achieve higher productivity with fewer resources while maintaining quality.
Conclusively, integrating AI and emerging welding technologies presents new horizons, especially for industries working with advanced and highly sensitive metals that demand precise control during the welding process. As the industry advances, these innovations in welding methods are poised to enhance safety, elevate quality, and boost overall productivity. With AI and precise control driving new welding technologies, doors are opening in industries that demand top-tier weld quality for the latest and most intricate metals.
The welding industry is on the cusp of making significant strides in safety and quality as it continues to evolve and adapt to the ever-changing landscape of technology and innovation.
=========================
Dr. T.J. Prasadarao, Executive Director (Technical), D&H Sécheron.
“Sustainable welding techniques and consumables help reduce the environmental footprint of modern manufacturing while maintaining high production standards.”
Sunando Kumar Palit, Head – Strategy & Customer Experience, Ador Welding Ltd.
“Integrating AI and emerging welding technologies also opens fresh opportunities in industries with advanced and susceptible metals.”
Nimesh Chinoy, Director Sales & Marketing, SigmaWeld.
“Productivity and data analysis are the key drivers for welding technologies behind the transformative impact of welding technologies on the manufacturing industry.”
Vishwanath Kamath, Managing Director, Fronius India Pvt. Ltd.
“Integration of welding automation and robotics improves efficiency and safety, and growing demand for welding services generates demand for robotic welding experts.”
Ravichandran Duriaswamy, AGM- Product management, Messer Cutting Systems India Pvt. Ltd.
“Preparing metal for welding is critical to producing high-quality results, consistent productivity and minimising costs related to rework and downtime.”
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.