Sustaining the cutting needs of high end machines
By OEM Update Editorial January 11, 2019 5:00 pm IST
India is set to become a key player in terms of global machine tools industry and is likely to see substantial high-end machine tool manufacturing. Here, is an industry analysis by experts on how manufacturers are developing technologies in high-end machines, giving fruitful results in coming years and producing cost-effective machines.
The global push for IoT/ Industry 4.0 concept in manufacturing industries make its mandatory for machinery industry to develop and manufacture indigenous high-end machines that meets high performance and quality standards. This implies the Indian machine tool industry should review their present control technology, present mechanical design concepts implemented with a target for high-performance output.
With the initiation of ‘Make in India’ and easing of FDI inflow in key sectors such as defence and aerospace, the country has become a fastest growing manufacturing hub. The demand of high-end machine tools is also growing proportionately.
Military and defence sector fits right on the customised tooling manufacturing. Defence industry intakes components and machines in bulk which can be seen as positive indicator for both tooling and forming industry.
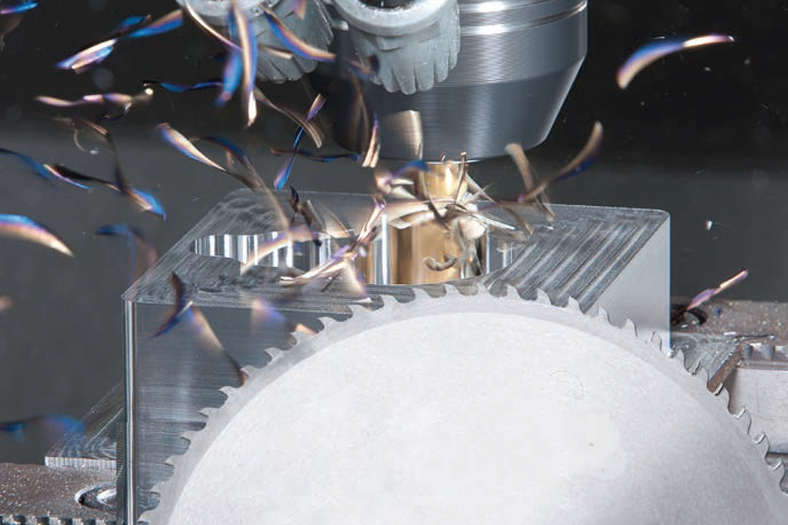
Industry demand is not getting fulfilled due to lake of penetration of robotic solution in metal cutting industry as compared to welding and other application. High-end machine, as the name signifies, are either large sized machine tools or high-precision in nature. The local demand of such high-end machine tools, in numbers, is always much smaller (10 per cent or less) than the total demand. To be viable, therefore, manufacturers of such high-end machine tools have to get adequate numbers from the international market through exports.
Metal cutting industry meeting the demands of high-end machine
Since the 90’s, when the Indian manufacturing industry took off, Indian machine tool manufacturers naturally had to first concentrate on the large volume of domestic demand because high-end manufacturing requires very high investments too. Besides, export of any machine tool requires deep pockets to support and sustain the export sales & services.
Ajay Gurjar, Dy. COO & Head, Business Operations says, “Currently, all cutting process which are enabled with robotic technology are best examples of high end cutting machine. Our robots were used for direct cutting application through CAD model which reduces the effort of people to program.”
Strategies to potentially meet the demands of high-end machines
High-end machines have the capability to manufacture high complex profiles combining various manufacturing processes into a machine. Such machines are good at multi-tasking, are predominantly larger in size and designed for bringing out high precision products.
V. Anbu, Director General, IMTMA says, “Indian machine tool industry needs to tap both Indian and overseas market by offering high-end machines at reasonable costs. For this, the industry needs to produce machines that are cost-effective.” Machines which can give a 30 – 40 per cent savings as against the high-end machines produced by other countries will definitely be an advantage. Indian technology is developing rapidly with the establishment of the Centre of Excellence at IIT-Madras. Manufacturers are developing technologies in high-end machines and this would give fruitful results in coming years.
India stands twelfth underway and eighth in the utilisation of machine apparatuses on the planet according to the 2017 Gardner Business Media overview. The country is set to become a key player in the global machine tools industry and is likely to see substantial high-end machine tool manufacturing. With emphasis on Make in India and manufacturing growth, the machine tools sector serves as the mother industry.
Gurjar says, “Robotic automation is the best way to empower the metal cutting industry to meet the high end machine demand because of robot can be used for big part cutting where hard automation may not provide the ROI.” Robot technology will increase; however, automation will not be only limited to robots. Automation extends beyond robots and there will be increases in integration of simpler automation solutions with metal cutting machines too. This will make a big impact in productivity, quality and safety. These simpler solutions will include tool pre-setters, pallet changers, machine tool probes, inventory management systems and tool condition monitoring systems.”
Also, when it comes on not contact type cutting like laser, plasma, water jet Robotic solution will be best in class most flexible solution and require to meet the demands of high end machine market.
CAD/CAM strategies to empower the metal cutting industryVineet Seth, Managing Director – South Asia & Middle East, Mastercam APAC suggested the following adoptions for a better process as well as an efficient workflow, in relation to CAM:
Wizards/process oriented workflow
Most CAD and CAM tasks today are driven by wizards. These wizards are typically process oriented and follow a structured way of achieving the desired results. These wizards also incorporate best practices, that ensure that even novice users are able to quickly learn and apply these processes on complex parts within a very short period of time.
Toolpath strategies
Toolpath strategies allow for CNC programming of the most complex of parts, using a graphic representation of the kind of toolpaths that will be generated upon applying a specific strategy. This allows the programmer to have a visual approach to toolpath generation. Further, through form based controls, strategies encompass various parameters that can be tweaked by advanced users.
Knowledge-based machining
Amassing the experience of seasoned professionals in the industry and customer feedback over many decades, KBM allows for parametrisation of certain machining processes. Threading, grooving, slotting, pocket milling, blade machining etc are some of the examples of KBM, where the user need not worry about process knowledge. The software takes in to account the type of machining operation and creates roughing through to finishing operations in a very fast and efficient manner. The user need only define model, material, bounds and machine.
Simulation
Simulation is an essential part of both CAD as well as CAM. Not to be confused with CAE, simulation in the CAD sense means to virtually and visually show kinematics, movements and motions of parts and assemblies; in the CAM sense, it means to virtually and visually show kinematics, tools, parts, movements, paths, and collisions in a given machine tool environment.
Simulation allows for corrections in complex toolpaths to avoid collisions, unwanted air moves, axis transformations and undesirable motions, amongst others, before the part is actually cut on the CNC machine. This saves time and costly accidents on the CNC machine.
With emphasis on Make in India and manufacturing growth, the machine tools sector serves as the mother industry.
Ajay Gurjar, Dy. COO & Head, Business Operations
Machines which can give a 30 – 40 per cent savings as against the high-end machines produced by other countries will definitely be an advantage.
V. Anbu, Director General, IMTMA
Knowledge-based monitoring allows for parametrisation of certain machining processes.
Vineet Seth, Managing Director – South Asia & Middle East, Mastercam APAC
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.