Automating Safety
By Staff Report July 31, 2024 6:23 pm IST
Workman safety is a primary concern. AI and robotics are shaping operational fineness and automating manufacturing for safety. Factories are achieving new paradigms in safety using predictive maintenance, real-time data analytics and machine learning for quality control. These technologies are spiralling manufacturing processes to create a safer working environment, minimising accidents while reckoning industry demands for safety.
“A culture of safety is not a concept. It is a way of life.”- James David Power III, the founder of the data analytics firm J.D. Power and Associates.
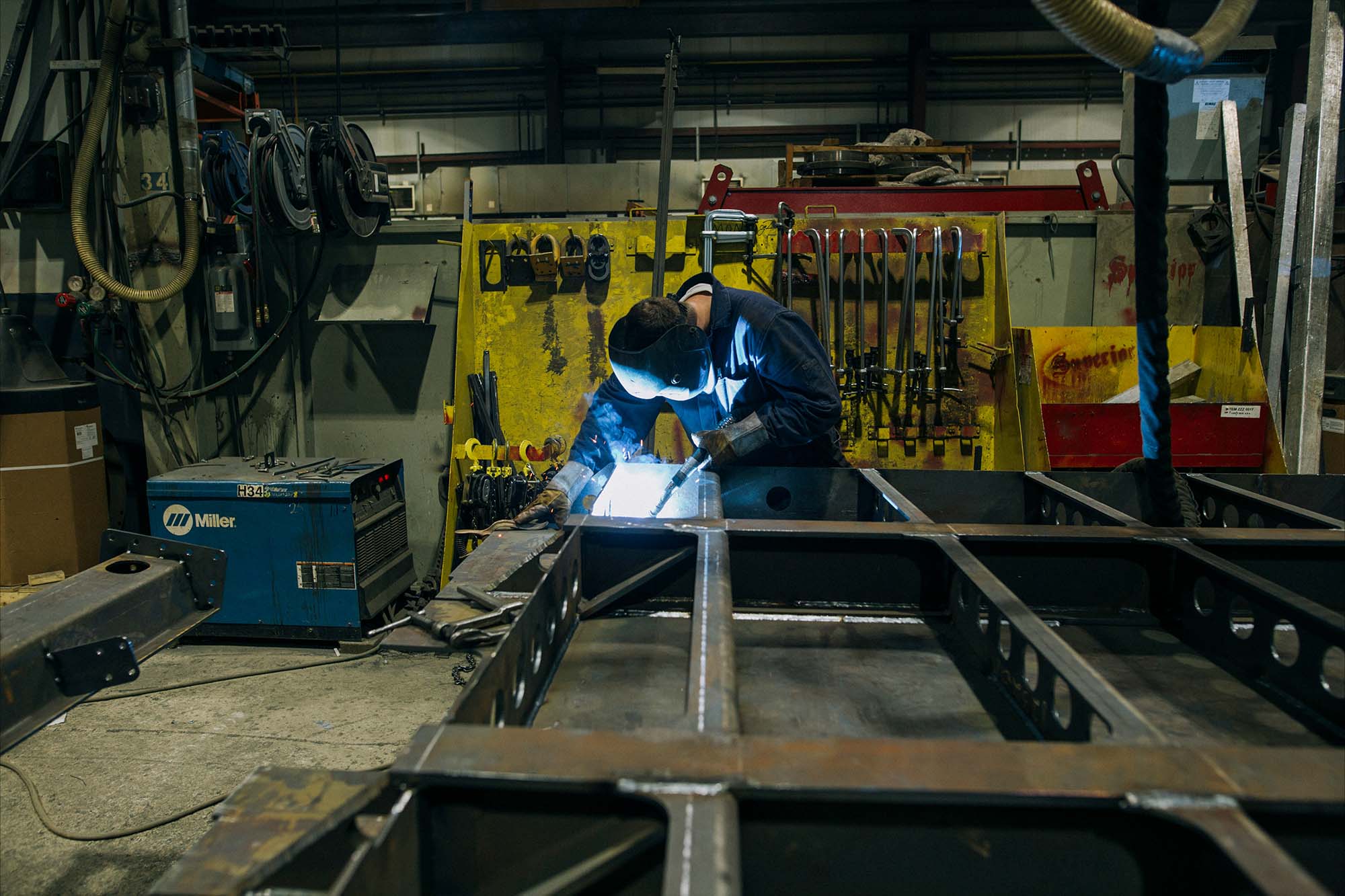
Industry 4.0 technology introduces new assembly methods for manufacturing operations and improved worker safety measures. Automation improves operational efficiency by streamlining manufacturing processes. Automated systems handle repetitive tasks, reduce human error and increase productivity. Robotic arms perform welding, painting, and assembly. This consistency speeds up production. Moreover, one of the aspects of automating factory manufacturing is the integration of real-time monitoring systems.
Monitoring and maintenance tools
The monitoring systems use sensors and IoT devices to collect data on performance, temperature, vibration, and other parameters. By analysing this data, predictive maintenance algorithms can identify potential issues before they cause equipment failure, leading to less downtime and maintenance costs. For instance, a vibration sensor on a motor can detect signals that indicate wear and tear, resulting in maintenance before a breakdown.
Preventive maintenance keeps machinery in optimal condition, extending its operational life. Sameer Gandhi, Managing Director, OMRON Automation, remarks that data-driven insights help determine the optimal maintenance times. That means a better return on investment. Sensors and AI monitor equipment health in real time, identifying potential issues before they lead to failures. All this leads to improved product quality, reduced downtime, enhanced safety, and cost savings.
Risk management
Automation improves risk management by providing quick solutions during crises. Automated systems can be programmed to shut down machinery and alert personnel in emergencies, such as fire, chemical spills, or equipment malfunctions. Automated technology can transform manufacturing processes and endear the highest safety standards. For instance, fire detection sensors can trigger alarms and send alerts to the control room and emergency services. This rapid response can mitigate damage and protect workers and the manufacturing facility.
Automation shrinks the need for human workers to perform dangerous tasks, lowering the risk of workplace injuries. Automated systems handle hazardous tasks like handling toxic chemicals, operating heavy machinery, or working in extreme temperatures. Robotic welding systems involve high heat and potential exposure to harmful gases to save human workers from risk. This shift improves worker safety.
Advanced safety controllers are also essential for worker safety in automated environments. These controllers manage safety circuits and emergency stop functions, providing protection.
AI and robotics for factory
The accelerating development in AI is redefining possibilities for industrial robotics. Robotics and AI impact automation by improving accuracy, efficiency and flexibility. Robotic systems with AI-driven algorithms enable autonomous decision-making, adaptive learning, and predictive maintenance in automation processes.
Robotic technologies, such as autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and collaborative robots (cobots), customise automation-related tasks. Dhiraj Podutwar, Business Development Manager at Pilz India, believes that robotic adoption in various industries will infuse exponential growth. The factories and plants focus on collaboration between humans and robots to increase the need for safety measures. Integrating robotics into existing manufacturing systems can be challenging. Addressing these challenges strategically, manufacturers can assemble robotics into their operations to improve productivity, efficiency, and safety, says Sameer.
AI integration into mobile robots, cobots, and other robotic systems provides speed, accuracy, and payload capacity. Subrata Karmakar, President of Robotics and Discrete Automation Division, ABB India, says these robots undertake a range of tasks in factories, warehouses, logistics and laboratory facilities. The future of AI and robotics for Smart factory solutions is optimistic and lends safety.
AI and machine learning are indispensable tools for enhancing safety procedures in the manufacturing sector. Expressing his views, Arvind Kakru, Vice President – Industrial Automation – Greater India, Schneider Electric, points out that by using these technologies, businesses can detect and address safety hazards, creating a safer environment for workers.
AI algorithms can detect anomalies to comply with quality standards. Dhiraj explains that AI-powered vision systems and machine learning algorithms enable robots to perceive and respond to their environment in real time. It provides credence for quality inspection, defect detection, and adaptive automation. AI and ML get factories to operate efficiently, improve safety, and deliver high-quality products. Furthermore, monitoring systems detect and correct any deviations. They use sensors and AI to do automated inspections, minimise human error and increase quality. To sum up, these technologies are meant to stay ahead of the competition and create a safe manufacturing environment.
Safety protocolsSafety protocols in the manufacturing industry are changing due to technological advancements, evolving regulatory frameworks, and industry initiatives. Industrial security involves safeguarding industrial facilities from intentional faults. With the increasing digitisation of factories, automated systems help to align with safety regulations and standards. By integrating safety features and controls, manufacturers can meet requirements set by regulatory bodies such as OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) and ISO (International Organisation for Standardisation). The safety lifecycle starts at the conceptual stage, and safety measures integrate into the design for the smooth operation of manufacturing processes.
Arvind emphasises that as technology advances and new regulations come into force, adherence to standards becomes essential. It results in a safe working environment and provides a framework for reliable manufacturing operations. Balancing these aspects is vital for the sustained success of manufacturing processes.
Upskilling
Automation in manufacturing also necessitates training and skill development for workers. Employees need to be proficient in operating and maintaining automated systems. They should also be capable of interpreting data from monitoring systems. This need drives upskilling and reskilling initiatives. The workforce gets prepared with the necessary knowledge and skills to meet the demands of automated manufacturing. Arvind emphasises that a safe working environment requires individuals to have the knowledge and skills to perform their tasks. Proficiency in these elements is needed to execute work duties and create a safe environment.
To think over
It is better to verify whether current safety measures for robotics are adequate. Implementing adequate safety standards is essential to protect workers. As humans and machines work closely together, efficiency in work practices improves. Automating factory manufacturing for safety involves utilising advanced technologies to create a safer and more efficient working environment. Here, predictive tools imply scheduling maintenance activities. By introducing real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, advanced safety controllers, and training programs, manufacturers can reduce risks and improve productivity. However, safe interaction between humans and robots requires new technologies and solutions. As the proximity between humans and machines decreases, the demands for safety rise. The industry must update its safety protocols to maintain compliance and enhance safety. Hence, regular maintenance is less expensive than fixing breakdowns.
==============
Sameer Gandhi, Managing Director, OMRON Automation, India.
Sensors and AI monitor equipment health in real time, leading to improved product quality, reduced downtime, enhanced safety, and cost savings.
Subrata Karmakar, President, Robotics and Discrete Automation Division, ABB India.
The future of AI and robotics for Smart factory solutions is bright, with AI-driven advancements enabling factories to become more flexible, efficient and safe.
Arvind Kakru, Vice President – Industrial Automation – Greater India, Schneider Electric.
By leveraging AI and ML technologies, businesses can proactively detect and address potential safety hazards, creating a safer environment for workers.
Dhiraj Podutwar (Business Development Manager, Pilz India Pvt. Ltd.
The factories and plants look at humans and robots working together to increase efficiency and productivity, so the need for safety is also a prime factor.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.