The four R’s of wastewater to be the new normal for industries
By OEM Update Editorial May 7, 2021 12:24 pm IST
This article walks us through the essential aspects of treating industrial wastewater by embedding latest technologies with utmost safety and security of wastewater treatment plants, industries and manpower.
India’s water and wastewater treatment market is projected to register a CAGR of 8.55 percent by 2026. Treating wastewater is an impending requirement for both industrial and residential purposes. Wastewater treatment is primarily carried out by technologies like preliminary treatment, primary and secondary treatment, tertiary and binary removal by biological treatment. Biological treatment technologies are primarily used to treat municipal water.
Wastewater technology trends impacting industrial facilities
In India, water is strength, freshwater is premium and going forward, recycling and reusing wastewater will be the new normal. From an industrial or a corporate perspective, some of the technologies have already been embedded to the processes. The government could have some discreet industrial level saying, the industrial waste cannot be discharged into the lakes or the rivers without treating them as prescribed by CPCB norms.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD) is another technological trend, which allows you to recycle and reuse the wastewater generated from various industrial processes, including sewage treatment plant to reuse them across industrial premises.
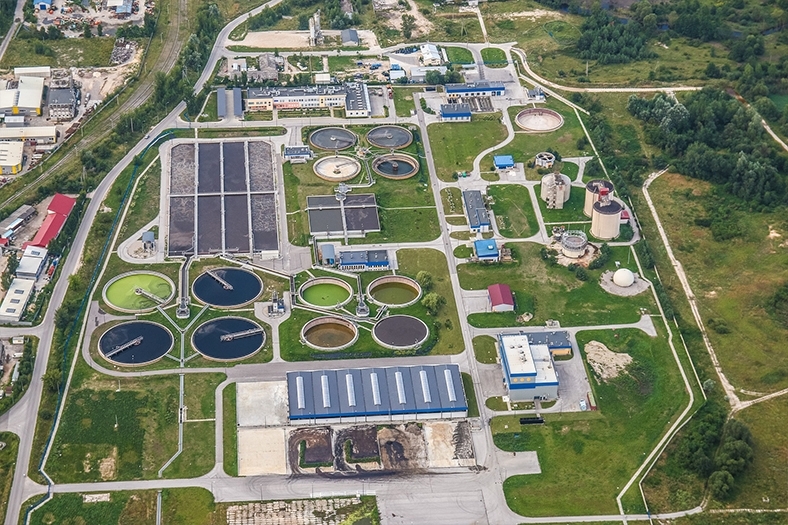
Common Effluent Treatment Plant (CETP), Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP), Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) are another essential technology. It aggregates all the effluence in a common effluent treatment plant, treats the water and market it back to the industry for their process needs. Even Grundfos’ Chennai plant has a ZLD system. Bangalore airport which is to buy a lot of treated water sewage treated water from the Bangalore corporation now has their own STP and then they recycle and reuse it.
Effective areas of utilisation
The wastewater generated is predominantly used for noncontact purposes, away from human consumption; at places like irrigation park, highway landscapes, residential landscape, fire protection, residential and corporate buildings. Recycled and recreated water is generally used in ponds and lakes. From an environmental perspective, you can use this water to create and enhance wetlands. This is predominantly done to improve the water table and use the groundwater.
Rangrajan R, Area Sales Director – Water Utilities, Grundfos explains the industrial standpoint. He says, “it can be used in cooling towers, industrial processes depending on the required type of treatment. It’s generally termed as tertiary treatment; this generally makes the water as good as potable that can be used in boiler make up water.”
At Grundfos, we use the recycled water for the effluent treatment plant. WE also have a CET also rainwater treatment or a water unit where the water that is used in the testbed goes to a sophomore recycled and then come back to the testbed. So, these are all some of the examples where you could efficiently and effectively use recycled water.
Safeguarding hygiene of manpower at plant level Every STP and ETP plant should have a standard operating
Every STP and ETP plant should have a standard operating procedure that defines the professional organisation. And, depending on the hazardous nature of the plant, somebody has to handle the raw sewage part or effluent part of the plant as they are toxic in nature. Appropriate personal protection equipment (PPEs) should be an integral part of standard operating procedures; and the operators should their optimum utilisation. The kit usually being used while working in the toxic environment includes; goggles, mask, gloves, safety shoes, and fire extinguishers in case any gas emanates during the processes.
Recycling and filtering process at plant levelTypically, there are four processes employed for a treatment; Physical Treatment, Chemical Treatment, Biological Treatment and Membrane Filtration – Tertiary Treatment.
Physical treatment does the cleaning and filtration of sewage water and removes the secondary solids. Chemical treatment has three processes – precipitation, cognition, and flocculation. These processes remove dissolved chemicals from the sewage water.
Biological treatment involves infusion of air because of the aerationto remove the demand of biological and chemical oxygen for all technical problems. This means we need to remove the dissolved biological metal like pathogens and bacteria among others.
Last one is the membrane filtration from the tertiary treatment. Here, a lot of filtration is used for salt reduction, and remove all the total dissolved solids in the water, and make the water potentially potable. In the secondary treatment, you can treat the water and discharge it into the lakes and ponds. With tertiary treatment, you can reuse the water for potable use, and for industrial processes.
Suggestions for effective wastewater management
Any water conscious industry should adopt water balancing techniques. Here, the entire idea is to understand how much you can recycle and reuse the wastewater generated. Also, with this process, we can understand how much freshwater is the protein you’re trying to release. For instance, one lakh litres of water is required for your industrial consumption and staff’s consumption. And then for other purposes, utility purposes. So, this one line of data is what is required per day if you put up a sewage treatment plant and effluent treatment plant. With this, if you’re able to generate about 60,000 litres of recycle and reusable water, you would need to purchase only about 40,000 litres. If the groundwater is too salty and you cannot use it, so that’s when you need to buy water through tankers. So, you would essentially save about 60,000 litres because you’re trying to recycle and reuse and that will certainly help you and your cost going forward.
When it comes to water factors or wastewater generation or production, we need to consider the four ‘Rs’ -Reduce, Recycle, Reuse and Recharge. Production of water is certainly going to be mandatory. We need to see how we can use some aerators in your tap and reduce the quantum of water. Further, they can be used for landscaping, plant mechanism, gardens to absorb water. We can always look at reducing the water stress and water consumption by not impacting the plant’s growth.
When we talk about recycling, it can be utilised for various purposes, or as a future compliant for different plant treatments depending on the kind of wastewater being generated. And then recycled and reused processes and other non-contact utility purposes. Last one is recharge; it’s all about rainwater harvesting and have percolation in your factory premises so that the groundwater improves to great extent, which in addition will give us surplus groundwater for the future. Grundfos’ Chennai facility, which is a green building and factory where the four ‘R’ principle well established for water balancing.
Innovative practices in treating wastewater
Let’s be more general, because, the entire country needs to adopt the recycle and reuse as a mechanism. In India, from an urban context, at least 37 percent of water is recycled and reused for multiple purposes, this is not sourced from the rural community. So, we have high quantum of water, sewage water that can be recycled and reused. If we start focusing on it, starting with rural because urban their government’s smart cities programme, through Housing and Urban Affairs Department. From an innovative standpoint, we also have great solutions to support, recycle and reuse these in the form of bait and system the control automation part. We have great solution efficient and effective.
To address the scarcity of water, the Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW), in association with the 2030 Water Resource Group (WRG) have been taking a couple of initiatives and decisions to enhance the wastewater treatment and management scenario in India. This includes investments in developing more water and wastewater treatment plants in the country.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.