Precision welding automation
By Staff Report August 30, 2024 4:18 pm IST
Technological advancements in laser cutting and welding, including high-power lasers with automation and Smart manufacturing, are transforming industries. The article highlights innovations in welding technology to improve efficiency, precision, and safety, aligning with the shift towards sustainable and intelligent production processes.
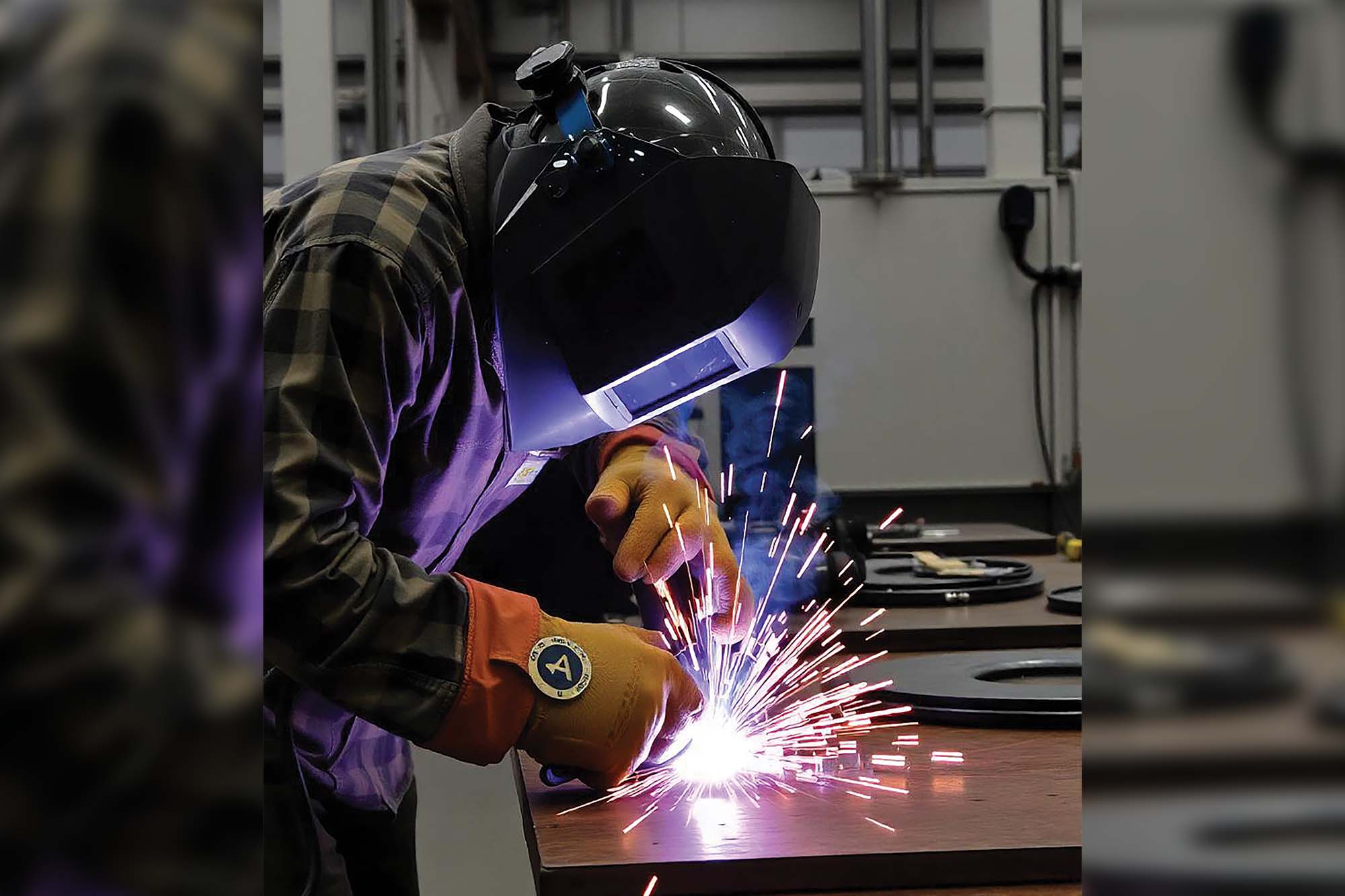
Welding is an essential part of the manufacturing industry. The global robotic welding market is expanding. According to a market intelligence report, the global market for robotic welding is growing from $5.80 billion 3 years before to $9.76 billion by 2028, with a CAGR of 7.7 percent. Also, the robotic welding equipment and peripherals market is projected to reach $11.57 billion by 2028 at a CAGR of 11.5 percent. Robotic welding trends include fixture elimination, automated sensing for quality, real-time data analysis and user-friendly cobots. The ongoing quest for efficiency leads to the development of operative welding techniques. Advancements in technology are improving quality and productivity. Technological progress and evolving industry needs drive laser cutting and welding technologies.
Laser welding and cutting trends
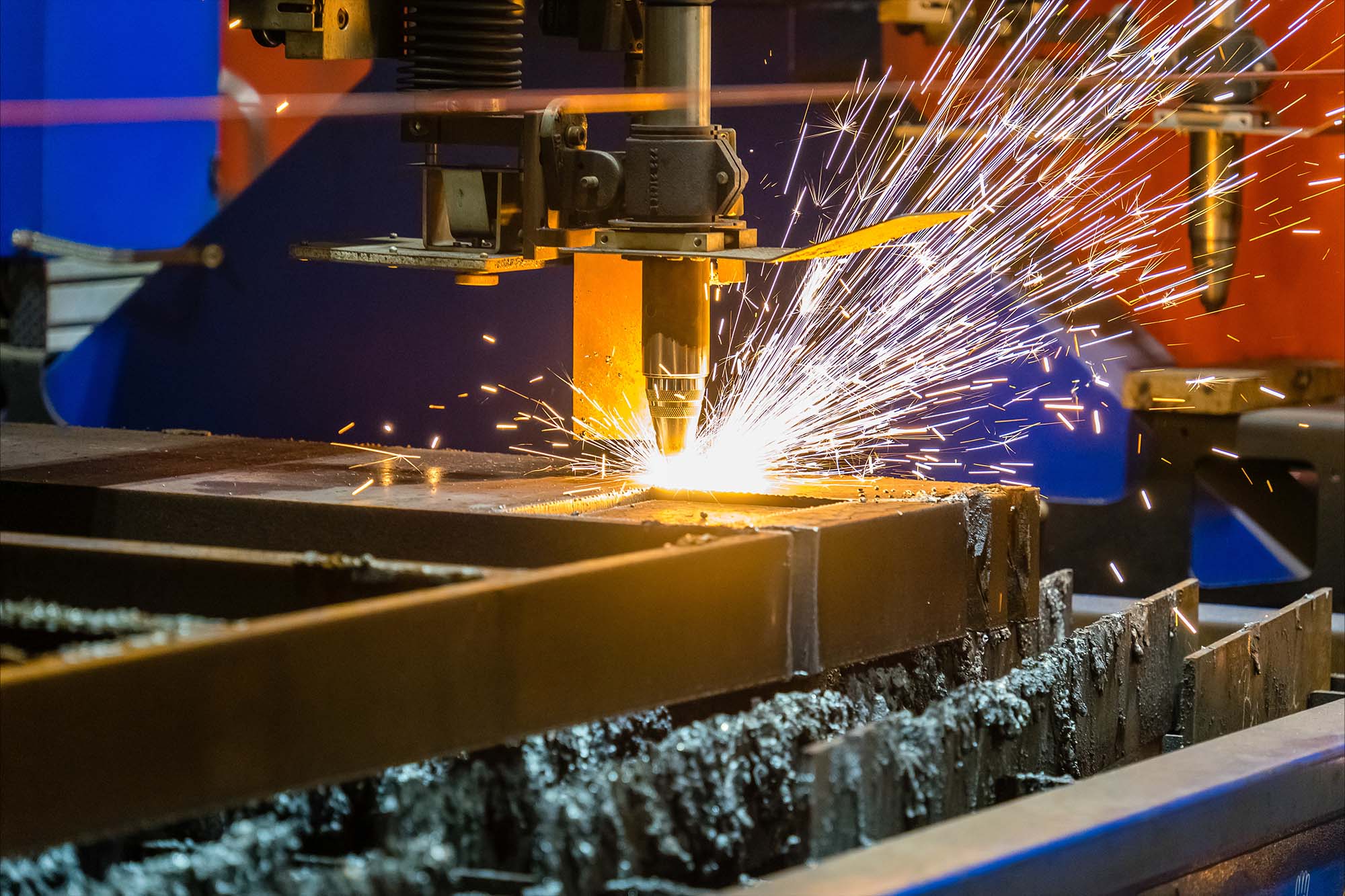
Laser welding and cutting technologies get impetus from technological advancements and industry demands. The adoption of fibre lasers trend is due to their energy efficiency, higher precision, and ability to cut and weld a wide range of materials. These lasers offer faster processing speeds and lower operational costs than traditional CO2 lasers. According to Sunando Kumar Palit, Head of Product Strategy & Customer Experience at Ador Welding, the rise of ultrafast and high-power lasers is another trend. Ultrafast lasers are the best for high-precision applications like microfabrication. High-power lasers are effective for cutting and welding thicker materials with speed.
The green and blue lasers are also gaining prominence for specialised applications with materials like copper. The 3D laser cutting and welding systems are expanding in automotive and aerospace because of their ability to handle complex geometries. Automation and Smart manufacturing are also becoming integral, incorporating robotic arms and automated systems for high-speed, precision operations. Rajeev Patki, Senior Product Manager at ESAB, highlights innovations like hybrid laser welding – combining laser power with traditional arc techniques – improving speed and usefulness in shipbuilding, transportation, and energy.
Welding automation
Automation lowers the dependency on skilled labour, reduces human errors and cuts costs. Optimising welding processes reduces waste and material costs and has a positive environmental impact through lower emissions and waste.
Dr. Krishnan Sivaraman, an industrial welding expert and Associate Dean at Fr. Conceicao Rodrigues Institute of Technology (FCRIT), highlights robotic welding as a prime example of how automation is reorganising the industry. Robotic welding achieves unmatched speed and precision, improving efficiency and reducing risks to human welders. A global shortage of skilled welders remains a challenge for the manufacturing sector. Companies must adopt industrial automation solutions like robotic and automated welding processes.
Automation in welding technologies brings incredible benefits, including improved productivity, cost reduction, and environmental sustainability. According to Sunando Kumar, automated systems adhere to precise specifications, ensuring higher-quality welds and making them useful for mass production, where exact repetition is required. Automation reduces downtime, increases manufacturing uptime, and accelerates production line efficiency. Moreover, advanced sensors and software monitor welding in real-time, allowing for predictive maintenance and reducing breakdowns.
India is now an attractive destination for foreign companies due to streamlined regulations, a skilled workforce, R&D opportunities, and the capacity to produce high-quality products. Industry experts and market analysts have dubbed the current phase the ‘golden era’ of the industrial boom in India, notes Dr. Krishnan.
Advancements in technologies
Training welders is often time-consuming, but virtual and augmented reality technologies enable safe training environments, reducing errors and increasing productivity. Innovations like laser sensing technologies provide real-time data and analytics, allowing workers to detect and correct welds more efficiently.
Dr. Krishnan notes that automation will not replace the manual workforce. The cobots are emerging, working alongside skilled welders to handle repetitive tasks and reduce human error while allowing welders to focus on complex tasks. Cobots offer cost-effective and efficient solutions.
Advanced materials, like high-strength steels and composites, are renovating welding processes, requiring new techniques and special training. Furthermore, shielded gas chambers help prevent oxidation and discolouration by creating a controlled, inert gas environment around welds, ensuring high-quality, corrosion-resistant results. AI and machine learning are enhancing welding technologies, optimising processes, and improving quality while promoting efficiency in industries dealing with sensitive metals.
Upskilling for future
As welding technology advances, there is a growing demand for skilled welders proficient in cutting-edge techniques. The American Welding Society forecasts a shortage of 400,000 welding operators by the end of 2024, driven by an ageing workforce, with the average welder 55 years old. This highlights the urgent need for continuous learning and upskilling to ensure a well-equipped workforce.The role of welders is shifting from traditional manual tasks to operating sophisticated, automated equipment. The advent of automation in welding means that welders now need to focus on operating and managing robotic systems, rather than performing all welding tasks manually. This shift requires welders to develop new skills, including offline programming and robotic cell management. Creating a culture of continuous learning is crucial for adapting to these changes. Companies must invest in upskilling their workforce to stay competitive in the global market.
Training with new technologies helps welders stay updated. Addressing the challenges of upskilling welders involves several key strategies, says Sunando. With rapid technological advancements, it has become imperative to upskill welders to meet the demands of a changing work environment. Simulators and VR create safer training environments. The educational institutions ensure that advanced welding technologies are integrated into curricula, allowing new welders to enter the workforce with the necessary skills. Apprenticeship programs further bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Online courses and tutorials allow welders to learn at their own pace.
Industries are investing in training programs that focus on advanced welding techniques like robotic and laser welding and additive manufacturing. The Skill India Initiative provides specialised training on modern machines and certifications to validate welders’ skills and knowledge.
Augmented reality and virtual reality are transforming welding training. Safety protocols integrated into AR training emphasise the importance of personal protective equipment and emergency procedures, ensuring trainees can manage welding risks efficiently. Augmented reality can change how welding students learn the trade. In addition, the role of AI in welding is expanding, optimising processes and improving quality. AI-driven systems can enhance training by providing data-driven insights and automating inspections. Rajeev feels that investing in AI and training programs will help welders adapt to technological advancements, making them valuable assets in the face of technological advancements. The latest training methods and technologies are essential for developing a skilled welding workforce ready to tackle the demands of modern welding processes.
In a nutshell, the heavy manufacturing and welding automation industry is witnessing a transformative phase. Companies are navigating challenges through innovative solutions, adapting to the need for skilled workers and flexible production processes, and redefining the role of welders in the age of automation and technology.
===============
Dr. Krishnan Sivaraman, Industrial Welding Expert and Associate Dean, R&D and Industrial Liaisoning, FCRIT.
Robotic welding exemplifies automation impact, using computer control for unmatched speed, precision, and efficiency, reducing risks to human welders.
Omkar Bhise, Head, R&D Department, Universal Orbital Systems Pvt. Ltd.
Shielded gas chambers ensure cleaner welds, better appearance, and corrosion resistance for high-demand industries like aerospace.
Rajeev Patki, Senior Product Manager – Marketing, ESAB.
Investing in AI and training helps welders adapt to technological advancements, making them valuable assets in a tech-driven industry.
Sunando Kumar Palit, Head – Product Strategy & Customer Experience, Ador Welding Ltd.
Ultrafast lasers are best for microfabrication with precision high-power lasers cut and weld thicker materials quickly and accurately.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.