AI and Robotics safeguarding modern factories
By Staff Report July 31, 2024 5:48 pm IST
AI and robotics are taking over manufacturing plants for all the better reasons. Manufacturing efficiency and quality are improving, while workers are secured from potential hazards. Dhiraj Podutwar, Business Development Manager at Pilz India Pvt Ltd, shares the solutions they provide for further safeguarding machinery and processes.
How can AI and machine learning be utilised in factory automation to enhance production efficiency and quality?
The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), along with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), enhances factory automation. Predictive maintenance is one of the prime factors. AI algorithms analyse equipment data to predict failures. By identifying potential issues early, factories can schedule timely maintenance, minimising downtime. This approach safeguards critical machinery on production lines. ML models process vast production data in real time for efficient and smart quality control. They detect defects, ensuring that only high-quality products leave the factory. AI optimises production schedules and resource allocation. Factories can achieve safe and efficient automation systems by minimising waste and improving efficiency. Also, AI Algorithms can pinpoint anomalies, optimise packaging parameters, and adhere to quality standards.
AI-powered vision systems and ML algorithms enable robots to perceive and respond to their surroundings in real time, facilitating quality inspection, defect detection, and adaptive automation.
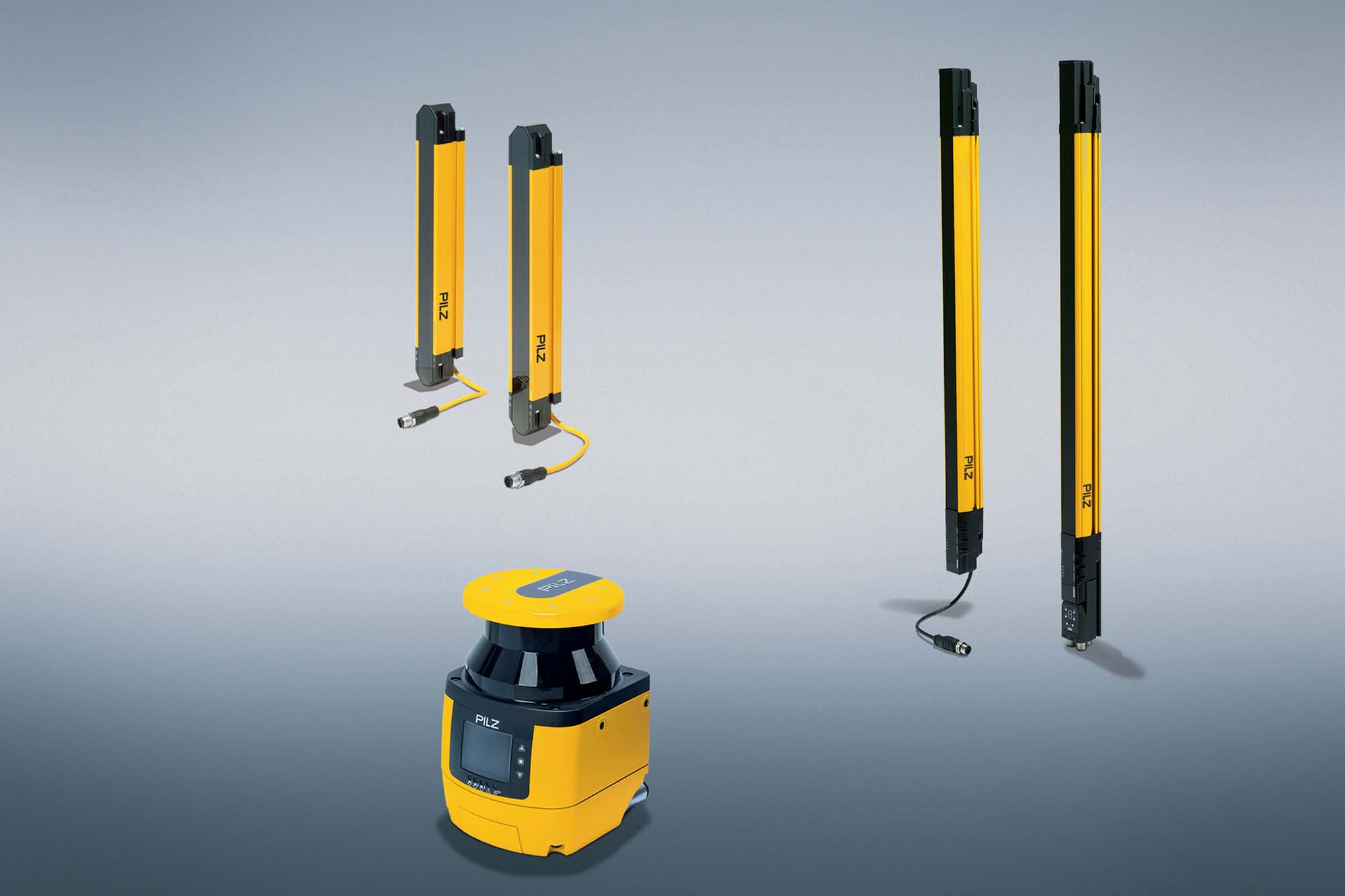

Why has the risk of industrial security increased with the digitisation of factories?
Industrial security protects production and industrial plants from faults. Systems are increasingly networked with the rise in digitisation, which heightens the risk of critical data being spied on or tampered with. Historically, communication in automation relied on field buses like CAN and proprietary protocols, meaning an attacker needed physical access or a modem-connected telephone line to cause harm. It is easier for cyber-attackers to intrude into automation and control systems, manipulate them and even compromise machinery safety. Motivation for the attacks ranges from terrorism, industrial espionage, and sabotage to extortion. The widespread use of open-source software and consumer-grade components in automation increases vulnerabilities, as attackers often know their weaknesses.
Data protection has gained prominence. Despite this, the importance of security should be appreciated. Essential security aspects and practical solutions help machine builders, plant designers, installation engineers, and maintenance engineers understand their role in customer security strategies.
Industrial security aims to guarantee the availability of plant and machinery and the integrity and confidentiality of machine data and processes. Moreover, functional safety is addressed, emphasising that security and safety are interconnected for safe production processes. Consumer products and complex operating systems in Industry 4.0 production plants must adopt automation. As IT standards cannot be directly applied, new standards like IEC 62443 have been developed to guide the step-by-step creation and implementation of a comprehensive industrial security strategy.
How do safety measures in robotics impact the production cycle times within the manufacturing process?
Robotics and artificial intelligence provide developed accuracy, effectiveness, and flexibility. AI-driven algorithms make autonomous decision-making, adaptive learning, and predictive maintenance possible. Numerous robotic technologies, including autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) and collaborative robots (cobots), customise automation-related processes. Robotic adoptions in various industries will continue to rise, with factories and plants looking at humans and robots working together.
The need for safety is increasing with the seeping of robots and cobots. Machine builders and factory operators need to ensure that the machine design complies with the relevant safety standards, such as ISO 10218-2 (Robot and Robotic devices – Safety requirement for industrial robots.), ISO 13849 (performance levels for robotic installations) and ISO/TS 15066 (Collaborative Robot and robotic devices). Robotics at Pilz consists of ROS modules for the industrial environment, service robotics, and the collision measurement set PRMS for human-robot collaboration (MRK). Pilz provides support to companies working towards safe applications.
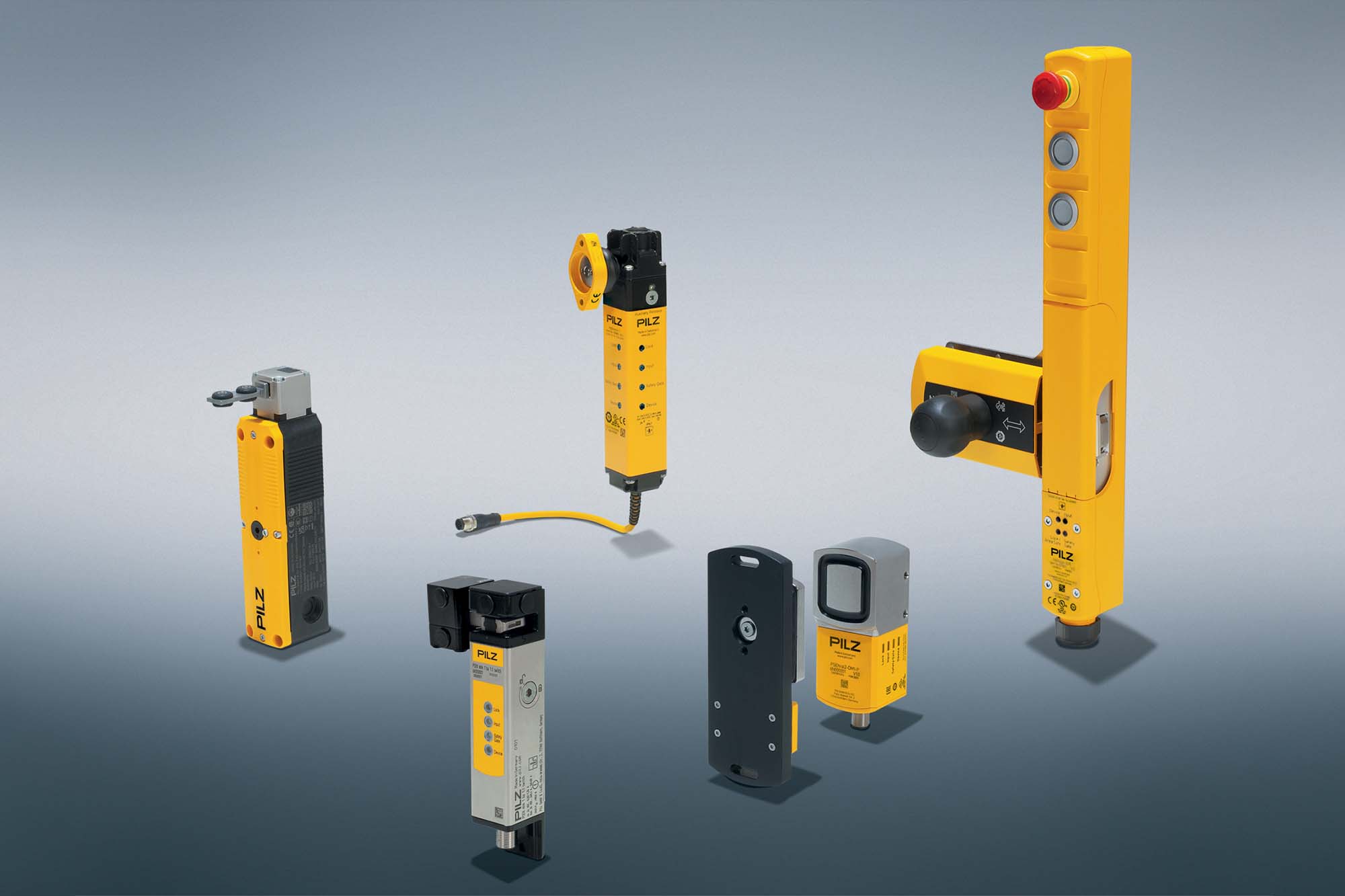

How does Pilz ensure machinery safety and industrial security with its product offerings?
Pilz offers a comprehensive range of solutions, beginning with advanced sensor technology that includes new products like the PSENmlock mini and PSENslock 2, safety switches with guard locking, and the range of products from Sensor’s family extends towards electromechanical switches and small safety switches, for specific applications. Our portfolio features safety light curtains used in the Packaging Industry, manual workstations, access guarding on conveyors or material handling alongside robots, where you can protect your staff and capital goods safely, efficiently and economically. They are used for finger, hand and body protection. Safety scanners are used in two-dimensional area monitoring. Due to the free configuration of warning fields and protected fields, along with the ability to adapt to structural conditions, the safety laser scanners integrate into the widest range of applications. The safety laser scanner PSENscan is especially suitable for stationary and mobile area guarding and access monitoring. We also have a safe radar system, providing robust protection across various scenarios. One can monitor protection zones safely even when optical sensors reach their limits with radar systems.
Pilz’s Sigma series and the modular safety relay myPNOZ stand out for their flexibility and ease of customisation in control technology. The PNOZmulti 2 family of small safety controllers, including the standalone and compact PNOZ m C0, offer powerful solutions for managing multiple safety functions. These controllers are best configured with the help of PNOZmulti Configurator. The renowned PSS4000 controller is designed to handle complex automation tasks reliably. Supporting these controllers, Pilz’s software tools PAS4000, used for the PSS4000 automation system, streamline configuration, programming, and diagnostics. The small controllers from the PNOZmulti 2 family are beneficial for integrating multiple safety functions into a single, cohesive system. The PSS4000 controller complements this by providing a robust solution for more complex automation needs. These controllers and associated software tools create a seamless safety network that ensures optimal performance and protection.
The Identification and Access Management (IAM) system incorporates the advanced PITmode fusion system technology for effectively managing access permissions. This ensures that only authorised personnel with RFID key authentication can operate machinery. It is used in Industrial Security applications and Modular Safety Gate Systems. In addition, IO-Link safety simplifies field-level communication, making factory automation more secure and efficient. Sensors can be integrated up to field level with the standardised point-to-point communication IO-Link Safety. IO-Link Safety also offers new possibilities for data diagnostics to optimise processes.
Overall, Pilz’s solutions, from sensor technology and control systems to industrial security measures, work together as a cohesive system.
How do we address challenges associated with integrating robotics into existing manufacturing to derive the benefits of robotic automation?
Robotics at Pilz consists of ROS modules for the industrial environment, service robotics, and the collision measurement set PRMS for human-robot collaboration (MRK). Before robotic integration, companies should look out for the probable hazards that can arise by integrating robots and existing systems. Verifying whether existing safety measures associated with robotics are sufficient is crucial. The closer humans and machines work together, the more efficient work practices become, and worker safety becomes important. However, safe interaction between humans and robots increasingly demands new technologies and solutions.
Integrating robotics into existing manufacturing systems can present several challenges, but with the right approach, the benefits of robotic automation can be fully realised. When assessing the risk with the robotics aspect, if a machine has already been accredited with CE marking, integrating a new robot can introduce new hazards. In such cases, a new CE marking is required, and a machine risk assessment must be carried out as part of this requirement. Pilz’s safety consulting services can assist with this process, ensuring compliance and safety.
Ensuring compatibility between new robotic systems and existing equipment and processes is another crucial step. Pilz provides safety controllers and sensors that seamlessly integrate with various robotic systems for safe operations.
Relevant robotic standards, such as ISO 10218 for industrial robots and ISO/TS 15066 for collaborative robots, ensure compliance and safety. Each robot application must be considered individually in terms of safety. Pilz provides support with a range of services tailored to the individual life phases of a robot system: From application analysis to risk assessment by EN ISO 12100 through to CE marking. Our safety solutions meet the specifications of DIN EN ISO 10218-2 and ISO/TS 15066. And to complete the range of services, we have a range of training courses on robot safety.
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.