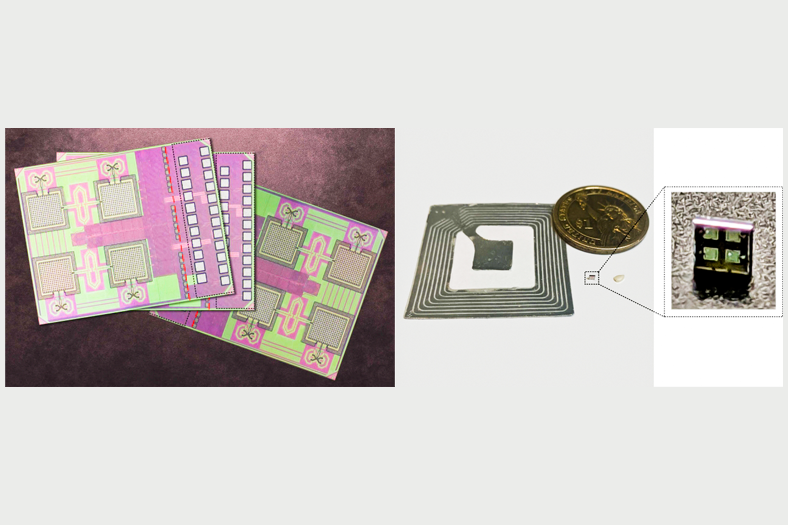
Cryptographic tag shows potential to protect supply chain
By OEM Update Editorial March 3, 2020 6:29 pm IST
Tiny, battery-free ID chip can authenticate nearly any product to help combat losses to counterfeiting.
To combat supply chain counterfeiting, which can cost companies billions of dollars annually, MIT researchers have invented a cryptographic ID tag that is small enough to fit on virtually any product and verify its authenticity.
A 2018 report from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development estimates that about $2 trillion worth of counterfeit goods will be sold worldwide in 2020. That is bad news for consumers and companies that order parts from different sources worldwide to build products.
Counterfeiters tend to use complex routes that include many checkpoints, making it challenging to verifying their origins and authenticity. Consequently, companies can end up with imitation parts. Wireless ID tags are becoming increasingly popular for authenticating assets as they change hands at each checkpoint. But these tags come with various trade-offs related to size, cost, energy, and security that limit their potential.
Popular radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags, for instance, are too large to fit on tiny objects such as medical and industrial components, automotive parts, or silicon chips. RFID tags also contain no tough security measures. Some tags are built with encryption schemes to protect against cloning and ward off hackers, but they are large and power hungry. Shrinking the tags means giving up both the antenna package — which enables radio-frequency communication — and the ability to run strong encryption.
In a paper presented at the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), the researchers describe an ID chip that navigates all those trade-offs. It is millimetre-sized and runs on relatively low levels of power supplied by photovoltaic diodes. It also transmits data at far ranges, using a power-free “backscatter” technique that operates at a frequency hundreds of times higher than RFIDs. Algorithm optimisation techniques also enable the chip to run a popular cryptography scheme that guarantees secure communications using extremely low energy.
“We call it the ‘tag of everything’. And everything should mean everything,” says co-author Ruonan Han, an associate professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and head of the Terahertz Integrated Electronics Group in the Microsystems Technology Laboratories (MTL). “If I want to track the logistics of, say, a single bolt or tooth implant or silicon chip, current RFID tags don’t enable that. We built a low-cost, tiny chip without packaging, batteries, or other external components that stores and transmits sensitive data.”
Joining Han on the paper are: graduate students Mohamed I. Ibrahim, Muhammad Ibrahim Wasiq Khan, and Chiraag S. Juvekar; former postdoc associate Wanyeong Jung; former postdoc Rabia Tugce Yazicigil; and Anantha P. Chandrakasan, who is the dean of the MIT School of Engineering and the Vannevar Bush Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science.
System integration
The work began as a means of creating better RFID tags. The team wanted to do away with packaging, which makes the tags bulky and increases manufacturing cost. They also wanted communication in the high terahertz frequency between microwave and infrared radiation — around 100 gigahertz and 10 terahertz — that enables chip integration of an antenna array and wireless communications at greater reader distances. Finally, they wanted cryptographic protocols because RFID tags can be scanned by essentially any reader and transmit their data indiscriminately.
But including all those functions would normally require building a fairly large chip. Instead, the researchers came up with “a pretty big system integration,” Ibrahim says, that enabled putting everything on a monolithic — meaning, not layered — silicon chip that was only about 1.6 square millimetres.
Pushing the limitsCurrently, the signal range sits around 5 cm, which is considered a far-field range, and allows for convenient use of a portable tag scanner. Next, the researchers hope to “push the limits” of the range even further, Ibrahim says. Eventually, they’d like many of the tags to ping one reader positioned somewhere far away in, say, a receiving room at a supply chain checkpoint. Many assets could then be verified rapidly.
“We think we can have a reader as a central hub that doesn’t have to come close to the tag, and all these chips can beam steer their signals to talk to that one reader,” Ibrahim says.
The researchers also hope to fully power the chip through the terahertz signals themselves, eliminating any need for photodiodes. The chips are so small, easy to make, and inexpensive that they can also be embedded into larger silicon computer chips, which are especially popular targets for counterfeiting.
“The US semiconductor industry suffered $7 billion to $10 billion in losses annually because of counterfeit chips,” Wasiq Khan says. “Our chip can be seamlessly integrated into other electronic chips for security purposes, so it could have huge impact on industry. Our chips cost a few cents each, but the technology is priceless,” he quipped.
For more information, contact:
Rob Matheson,MIT News Office
http://news.mit.edu/
Cookie Consent
We use cookies to personalize your experience. By continuing to visit this website you agree to our Terms & Conditions, Privacy Policy and Cookie Policy.